Luftwaffe Ground Force’s:
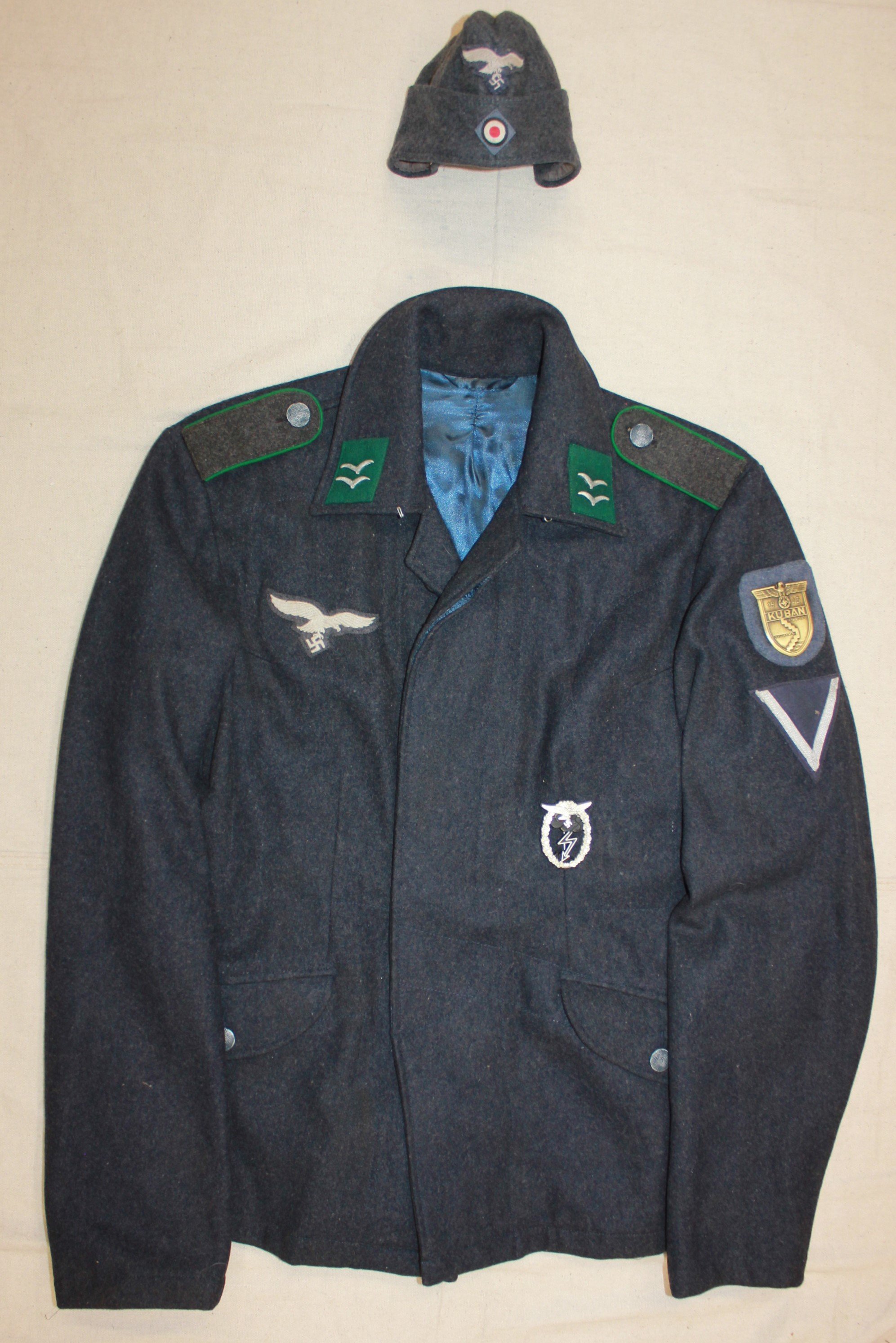
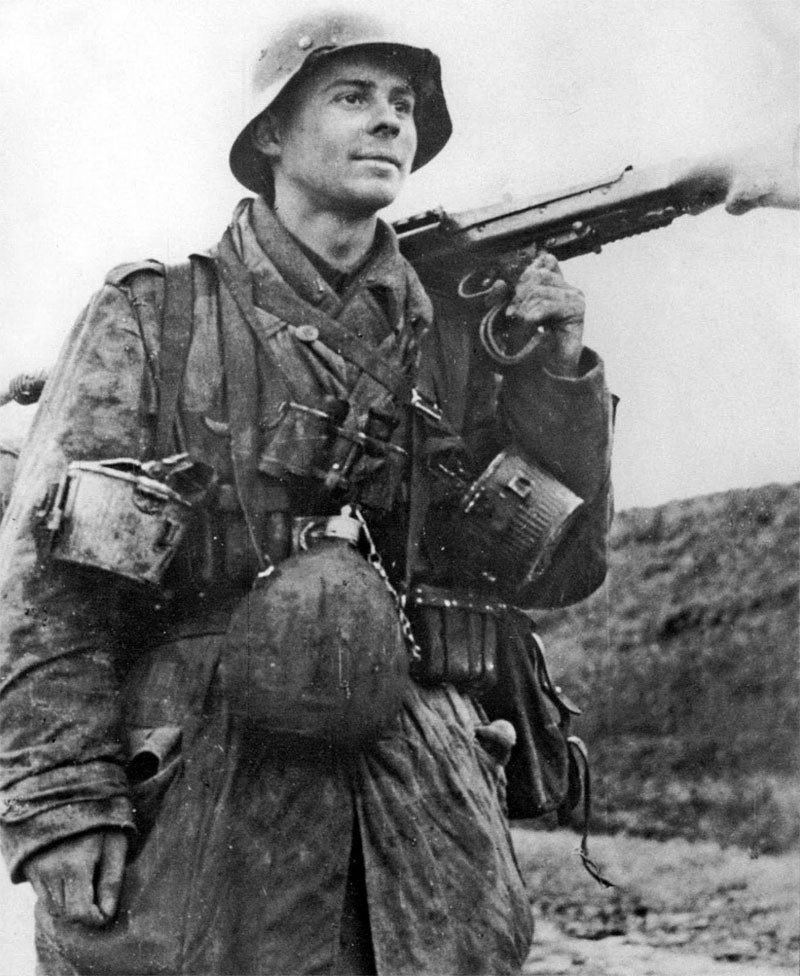
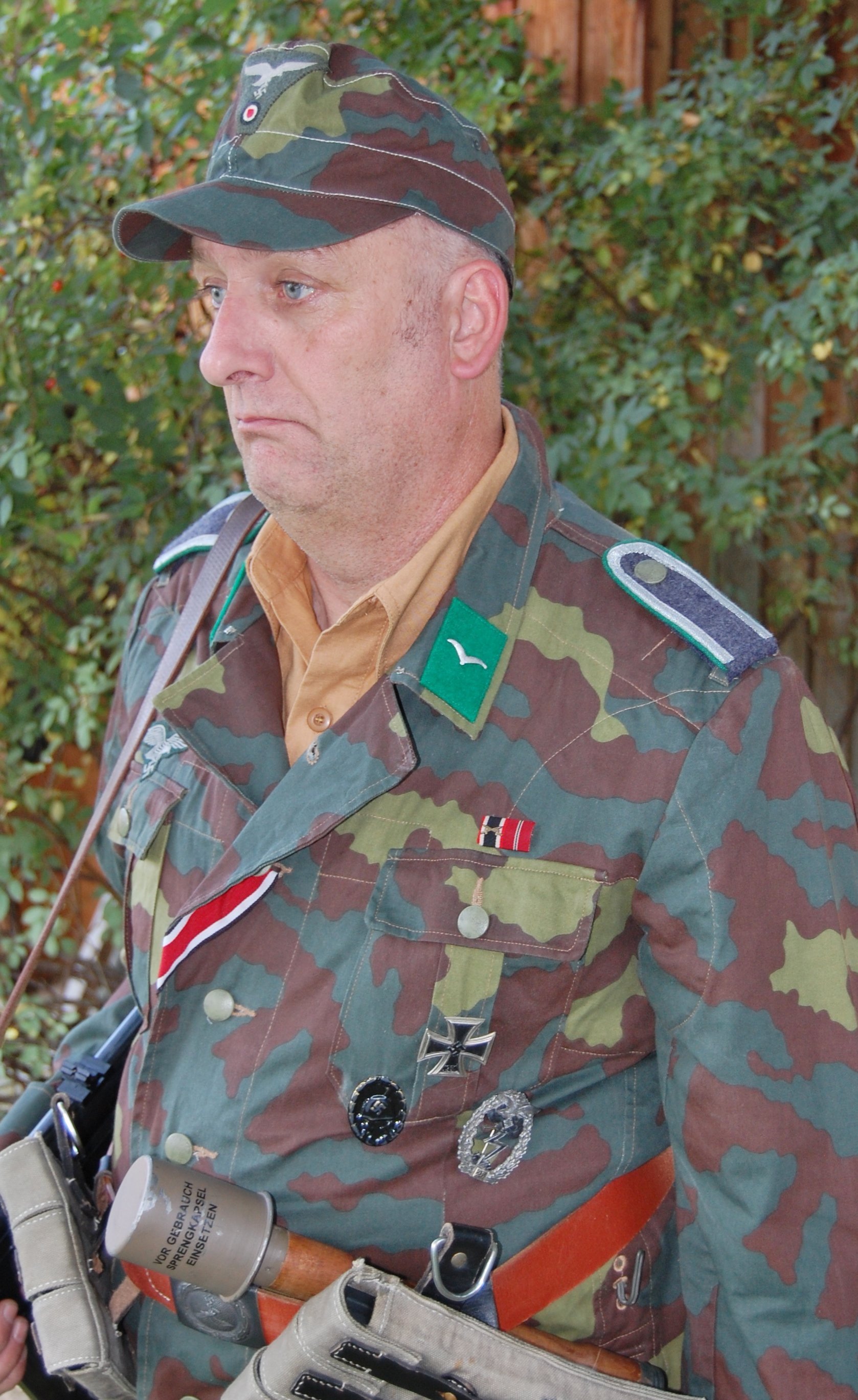
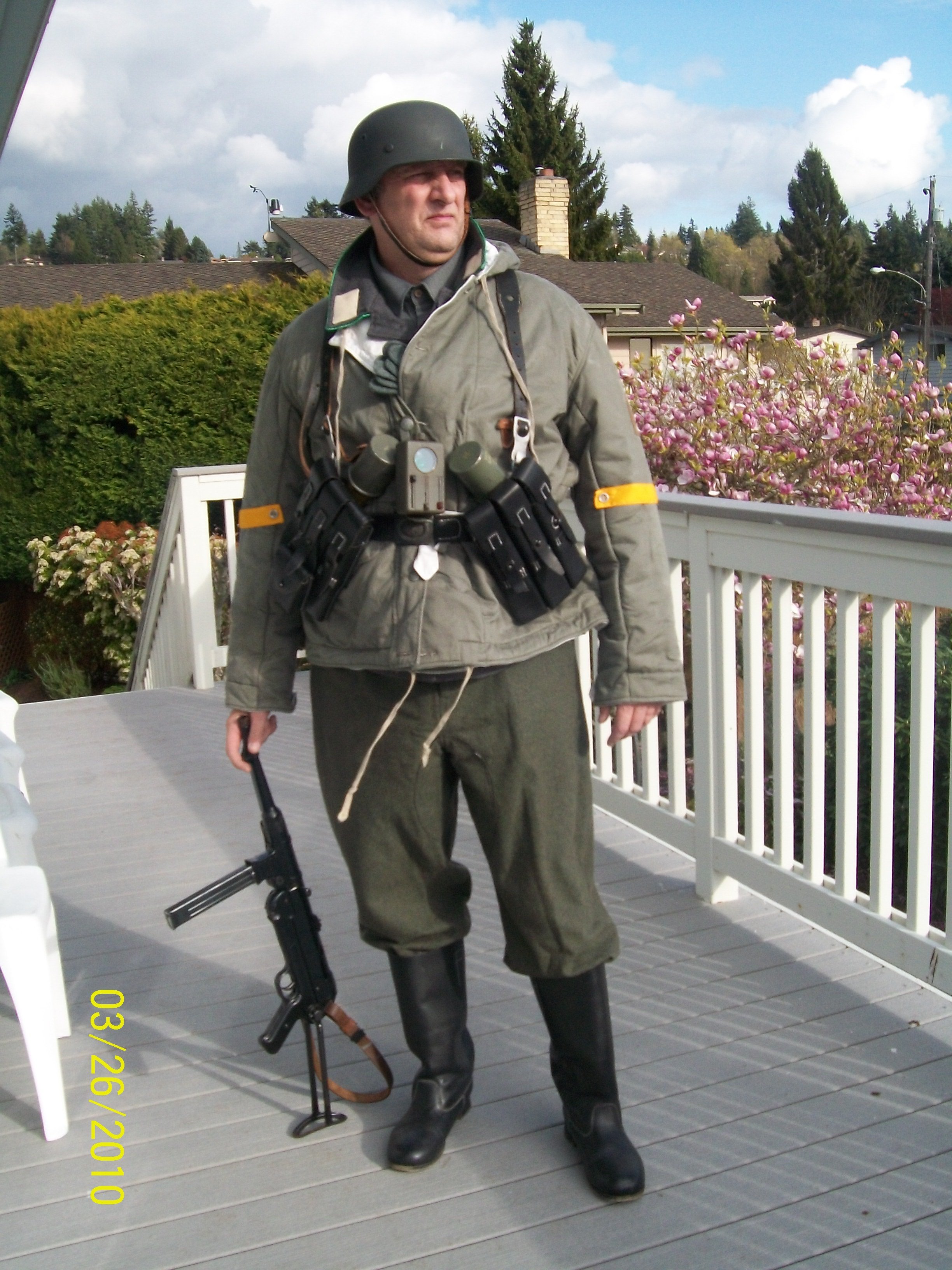
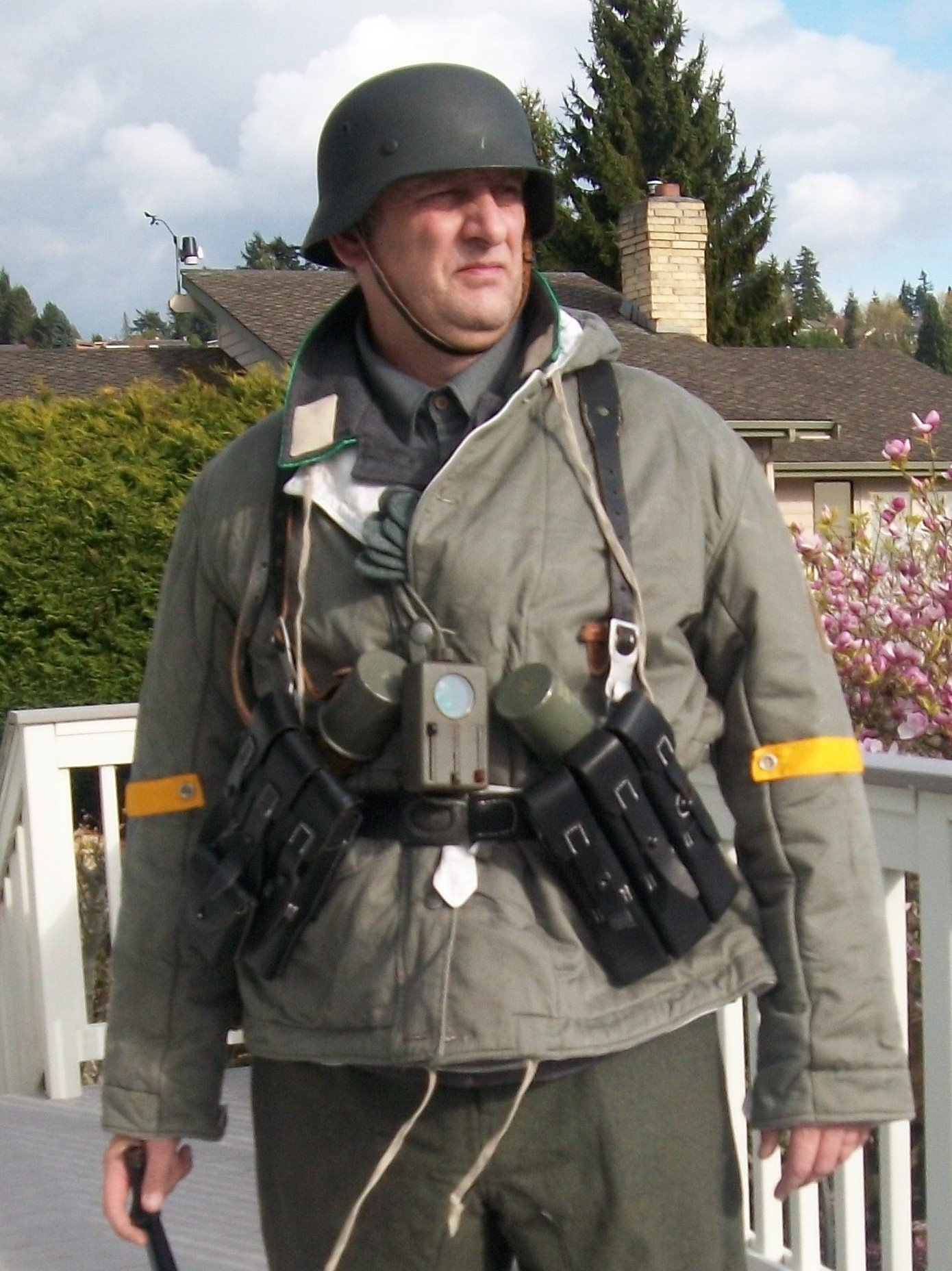
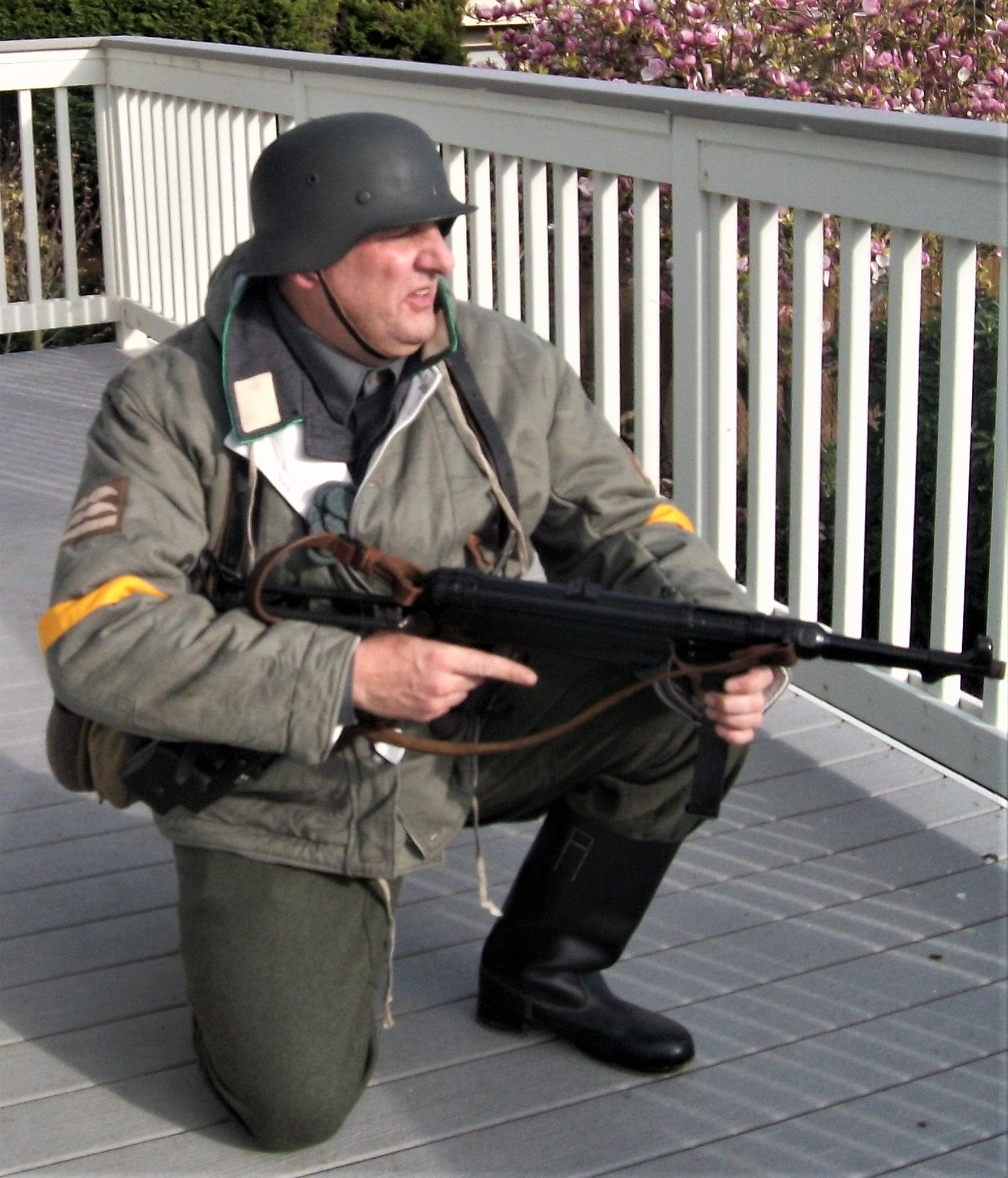
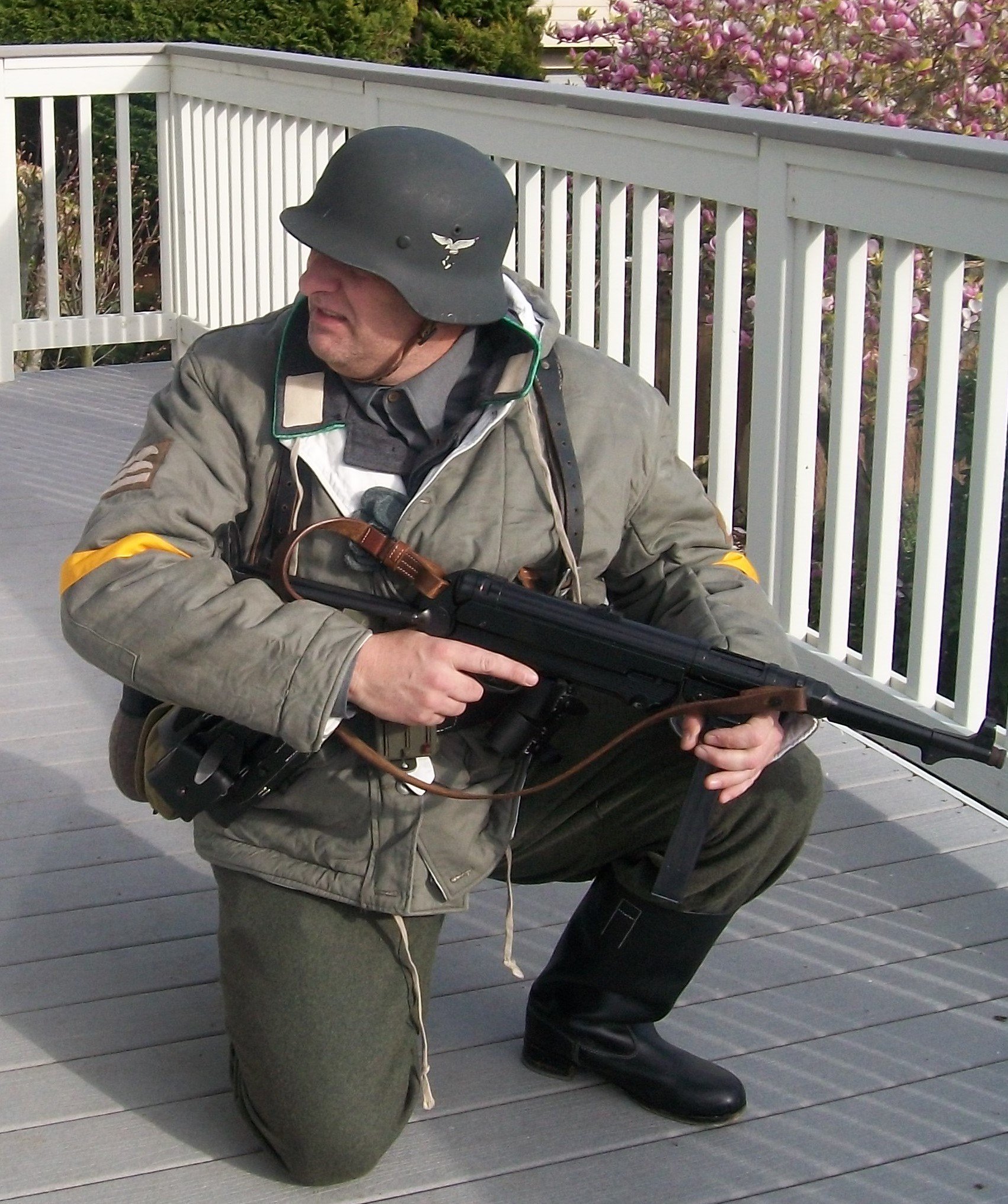
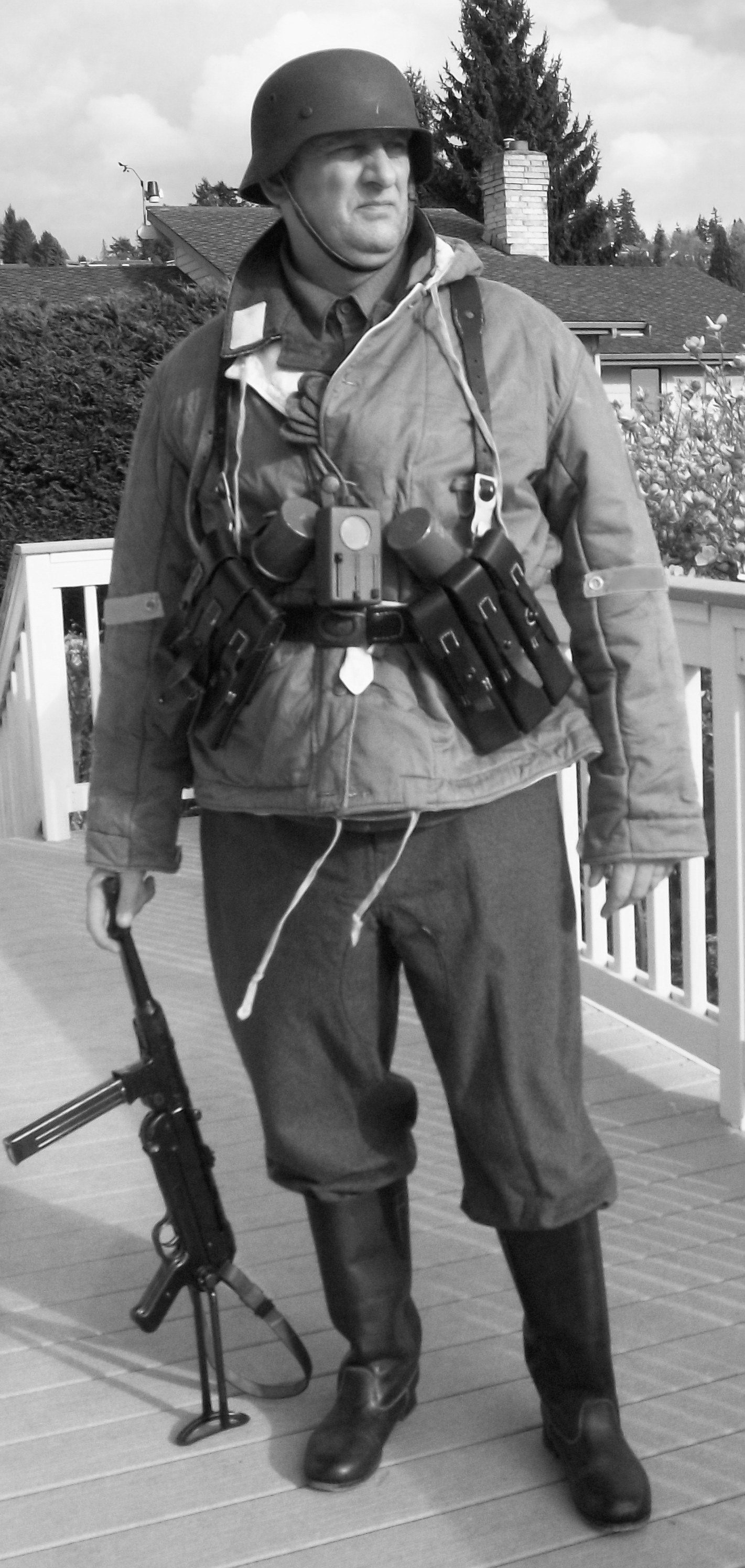
Gefreiter, 9. Luftwaffe Jäger Regiment, 5. Luftwafe Feld-Division:
5. Luftwaffe Feld-Division was formed in October 1942 under the command of Generalmajor Hans Joachim von Armin. Made up of surplus ground crew, it was intended to serve as a conventional infantry unit but under the Luftwaffe's command. (L). Returning to the front under the Romanian 3. Armee it in the Odessa Offensive until May 1944 when it was disbanded and personnel distributed to the 76.,320., u. 335 In fanterie Divisions. November 1943. Renamed 5. Feld-Division (L) was transferred to Romania for restructuring and refitting.
Infantry strength was reduced to one regiment. and it gained personnel from 9. u. 10. Jäger Regiments. Comprised of four Jäger (Licht Infanterie) Batallion (9. u.10 Regiments), one Artillerie Batallion, a single Sturmgeschütz, Pioneer, Nachtricthen, u. Versorgungs Kompanie it was deployed to Heeresgruppe Süd on the Ost Front. Initially serving in the Caucasus, it was withdrawn and fought around the Kuban Bridgehead from February bis April 1943. The following month, the unit evacuated to the Crimea.
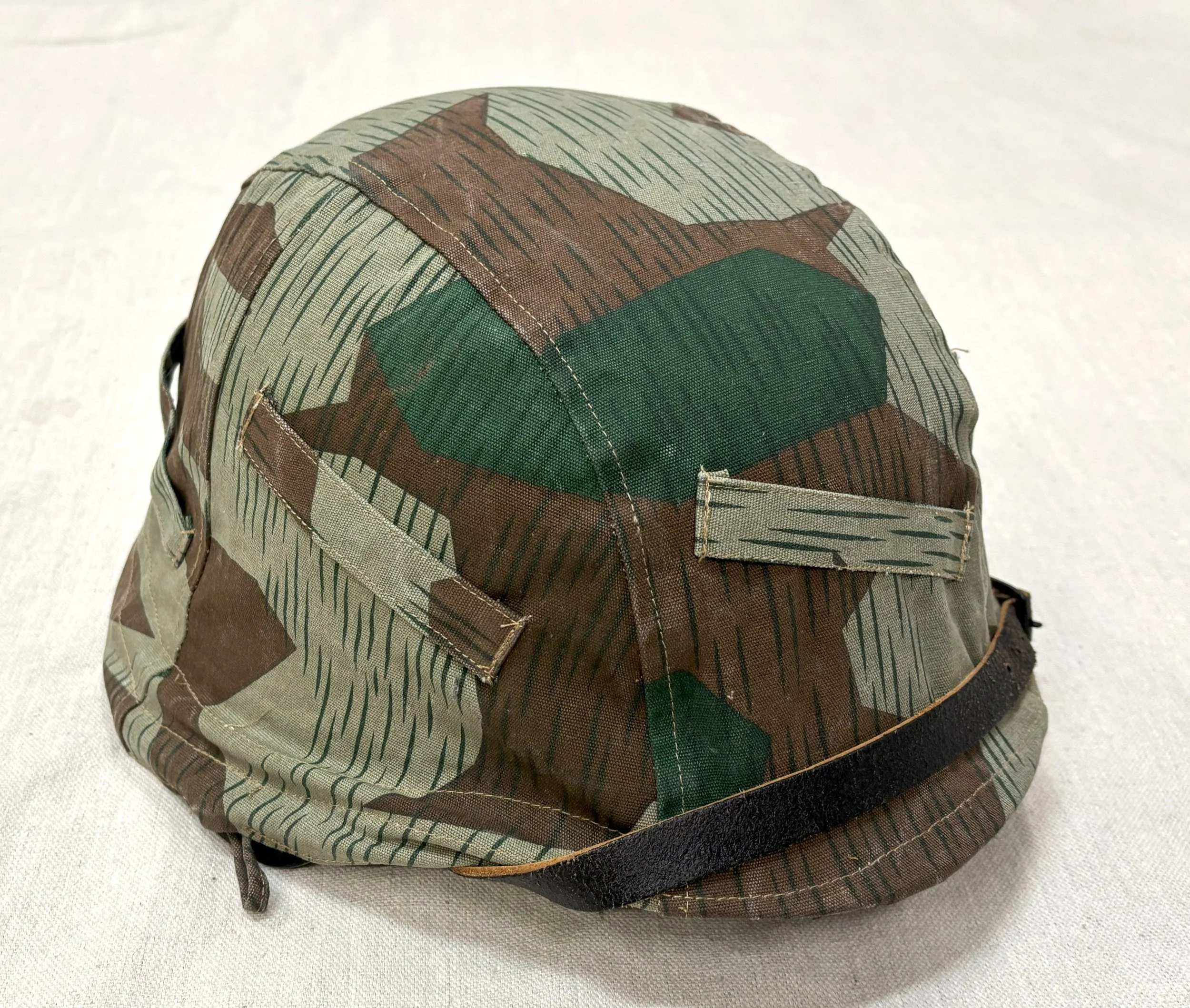
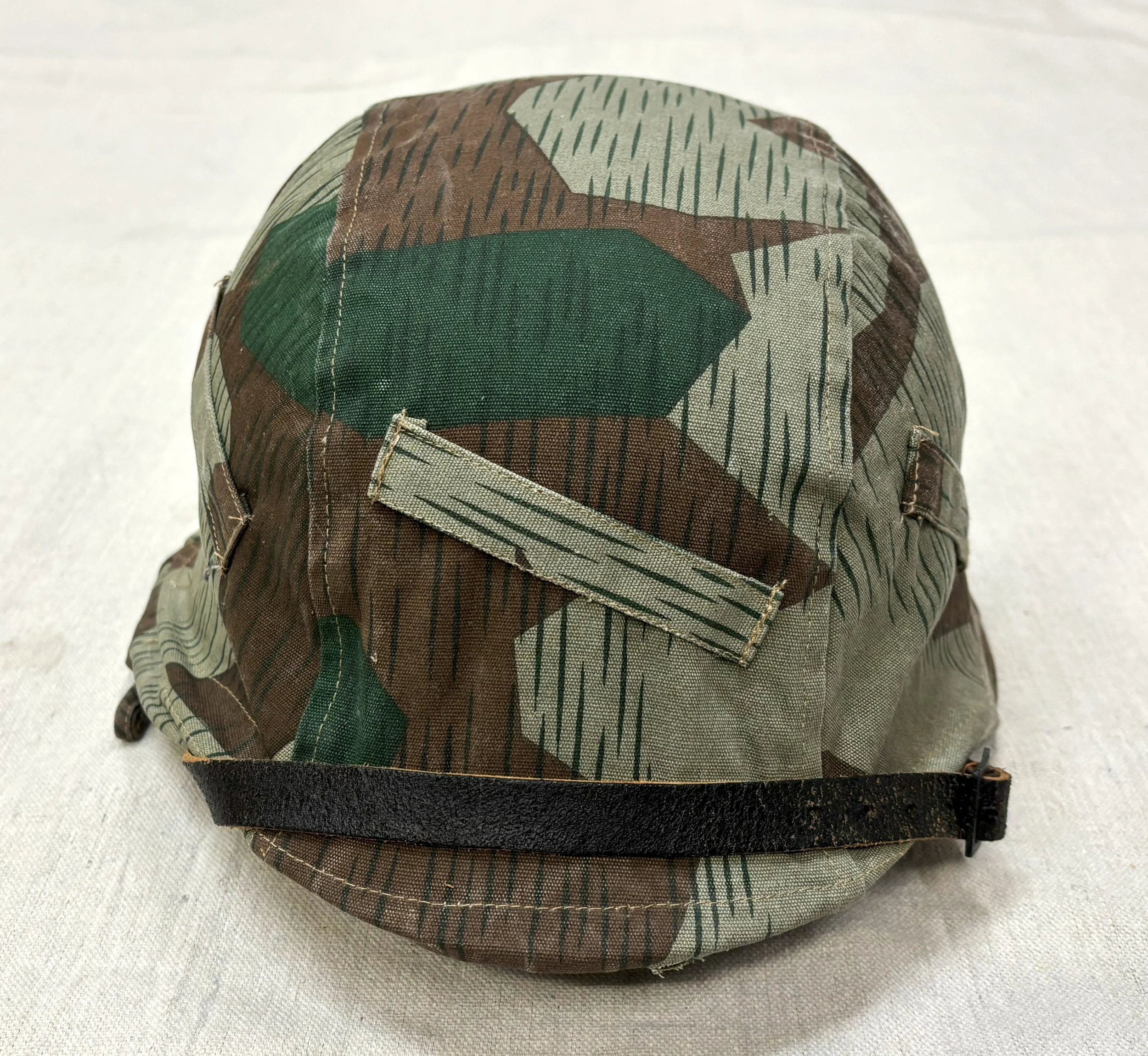
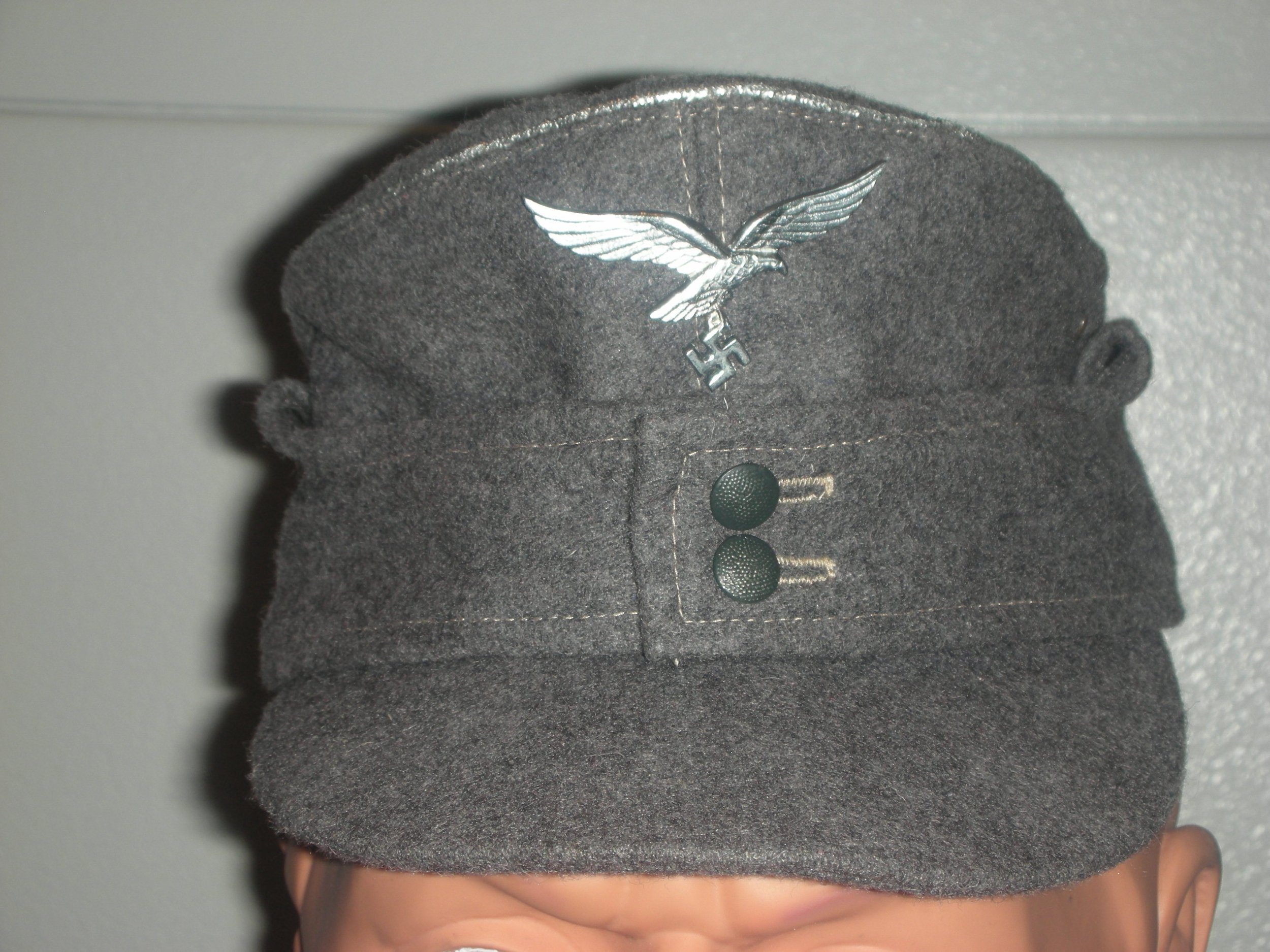
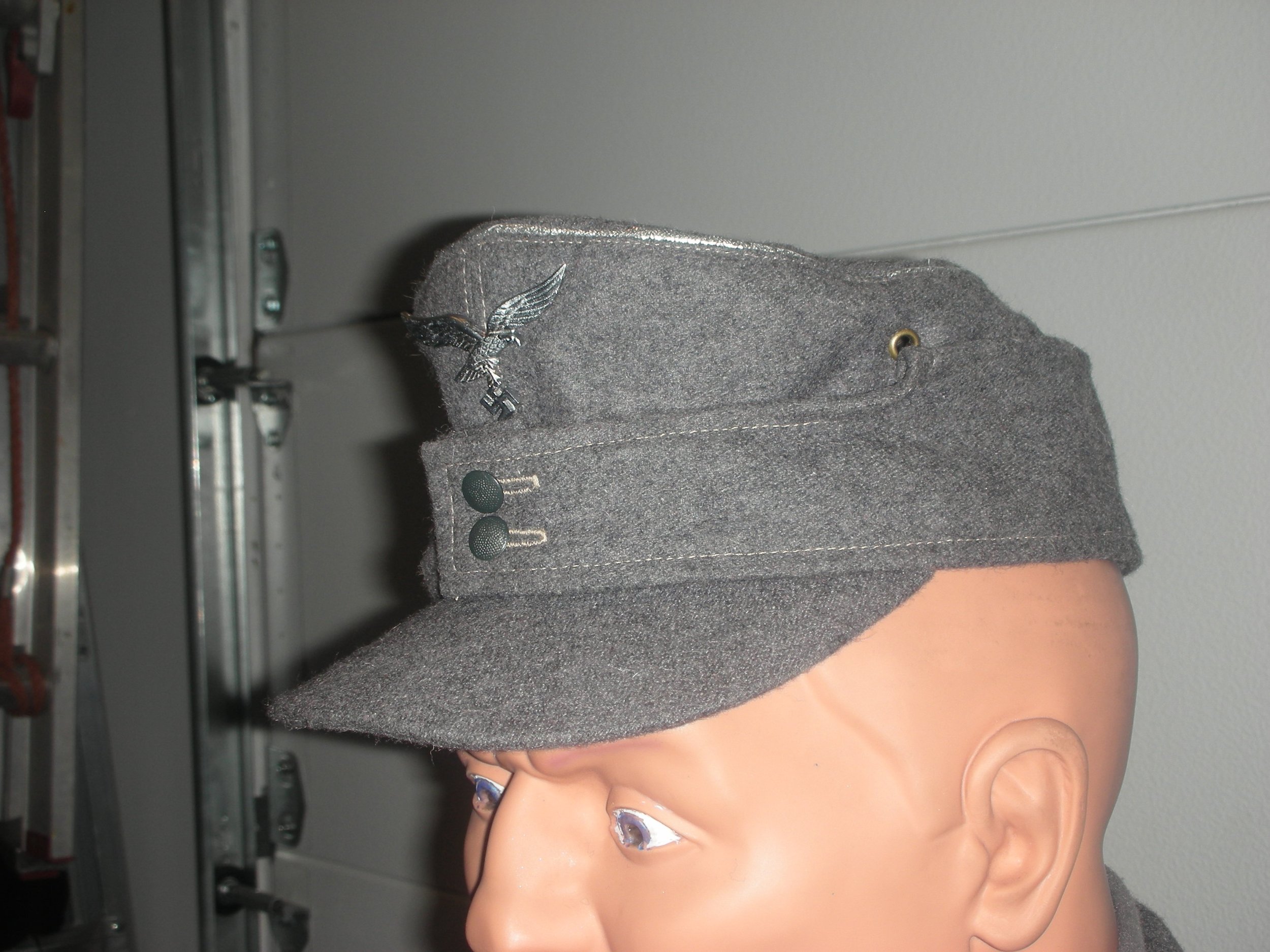
By the later part of the War, the dominant duty uniform was the Fleigerbluse worn here with the Gefreiter, it is a darker than normal blue-gray, possibly as the gray dye color was running out, and available blues were mixed in. The helmet I added it needed a home, and in this case, a re-issue, maybe, pre-war variant, because the cover is coming apart.
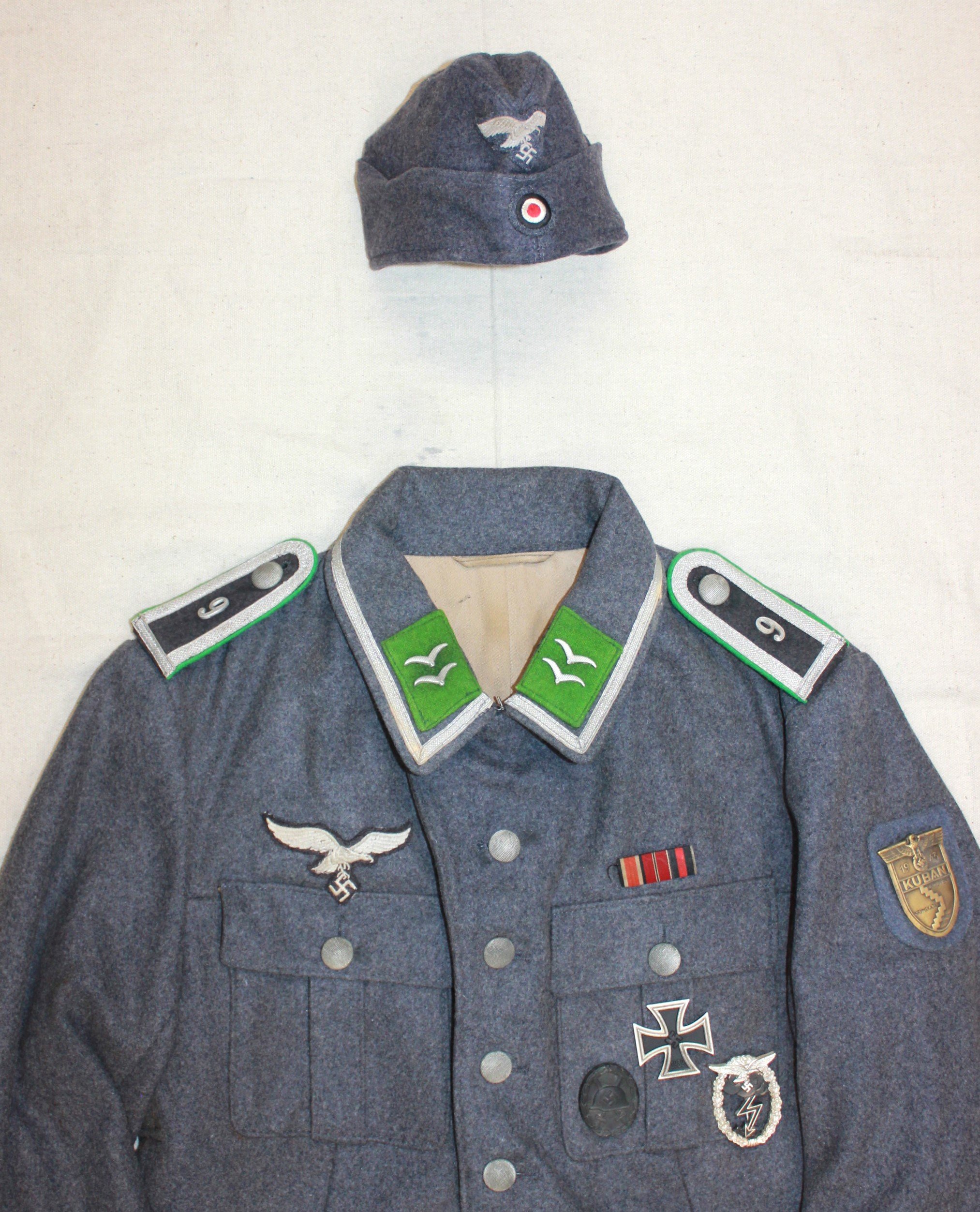
*Oberwachtmeister, 9. Luftwaffe Jäger Regiment 5. Luftwafe Feld-Division:
In September 1943, the division shifted north to Miletopol on the Panther-Wotan Line and suffered many casualties during the Battle of the Dnieper. Responsibility for the remnants of the division was transferred to the Heer in The Luftwaffe Truppen that made up the regiment came from varying branches and trades; none had been recruited initially as Infanterie Soldaten.
The original proposal from the Oberkommando des Heeres was to transfer these men to Heer divisions to be re-trained for the new role as combat soldiers. Reichsmarschall Goring had opposed this as it would reduce his Luftwaffe’s manpower as well as expose these more dedicated national socialists to the more monarchist-oriented Heer influence. He won the fight to keep them as Luftwaffe troops under direct Luftwaffe control.
This is the new home for these helmet photos. A lot of work taken to camouflauge this helmet, it’s pretty wild, with the colors over the cork-like texture over the top-its part of the paint.
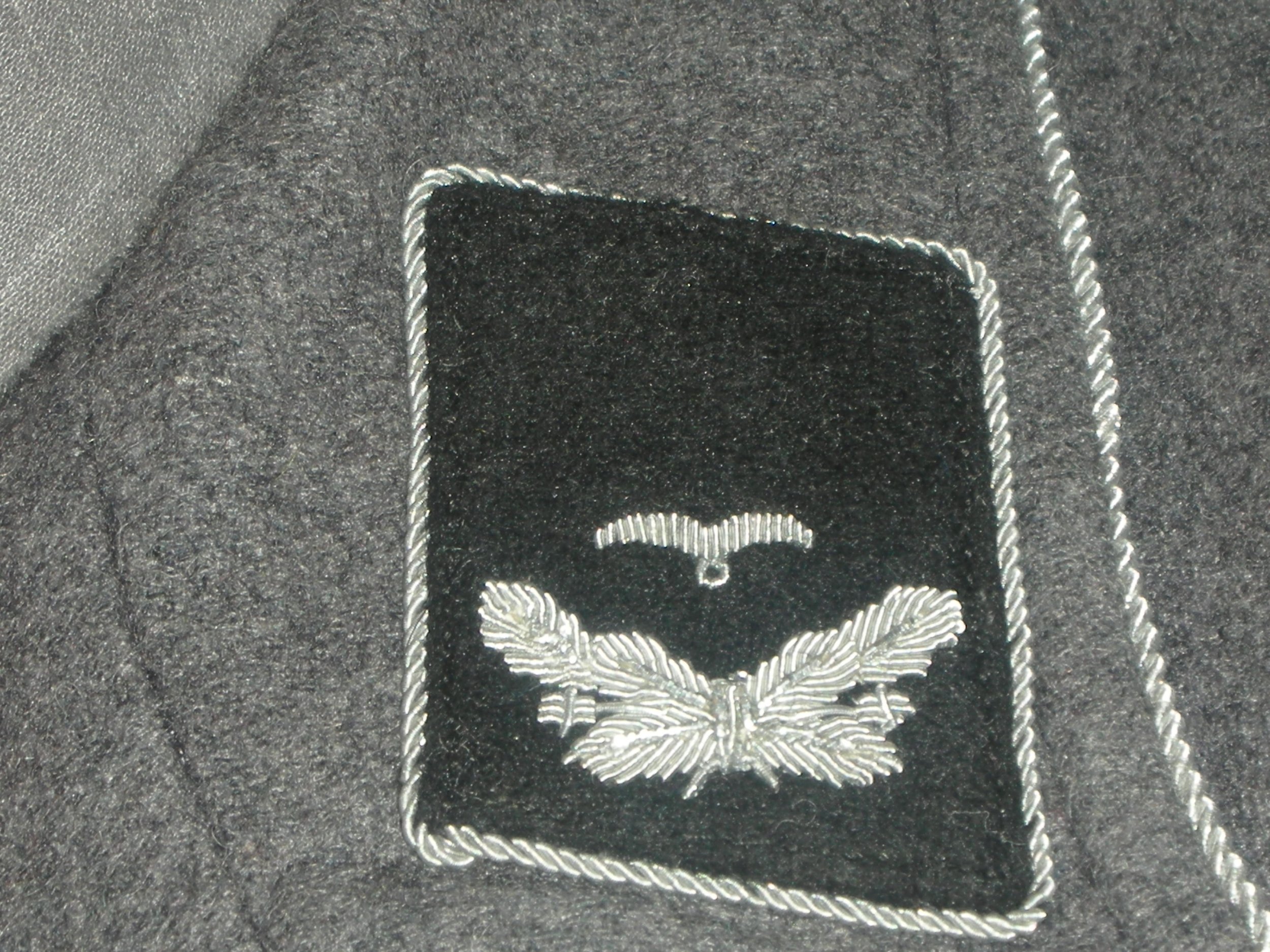
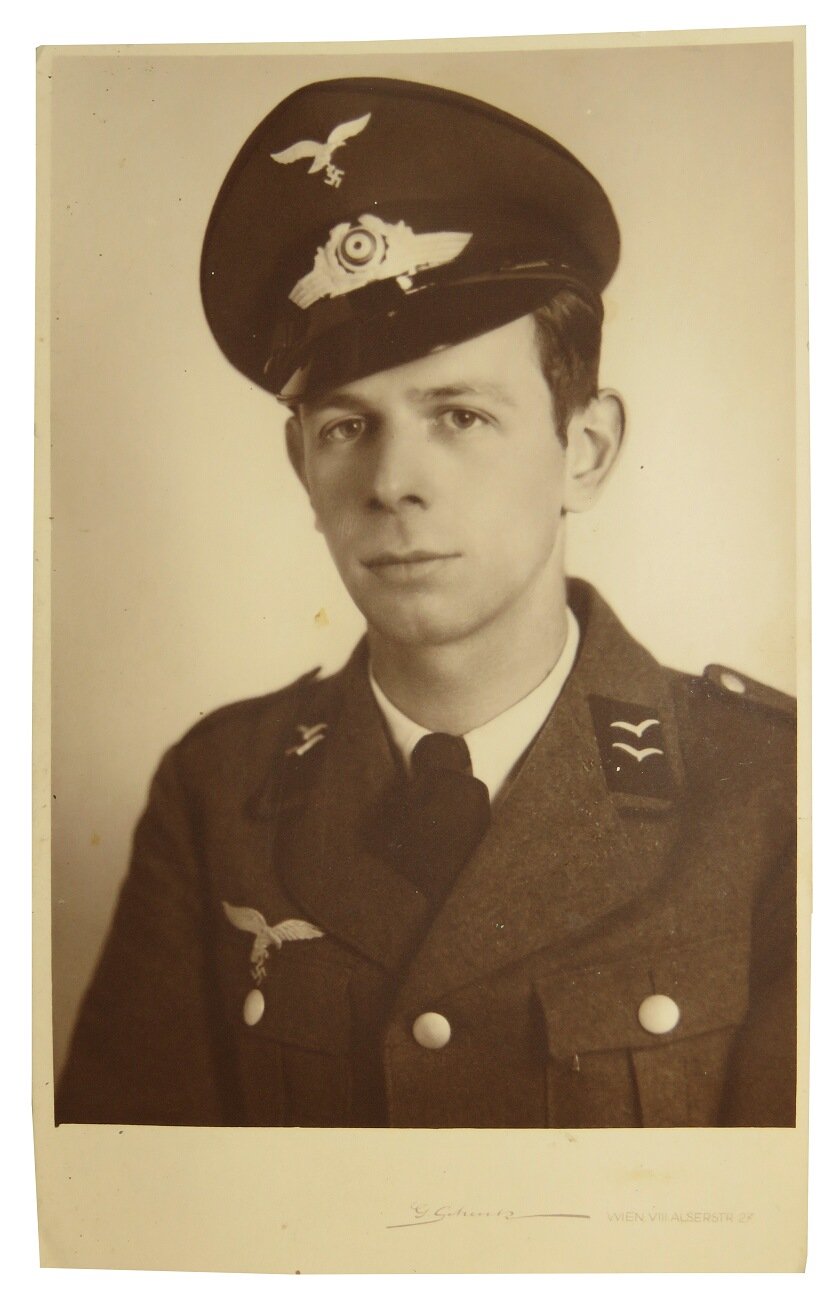
Feldwebel, 9. Luftwaffe Jäger Regiment 5. Luftwafe Feld-Division
The divisions were to serve in rear areas, releasing the Heer for front combat. This plan did not unfold as pictured, with most of the divisions thrown into the front line with only on-the-job training available. And thrown into the meat grinder of the East. There were precious few leaders who were up to that task, but the Gefreiter has taken on the task.
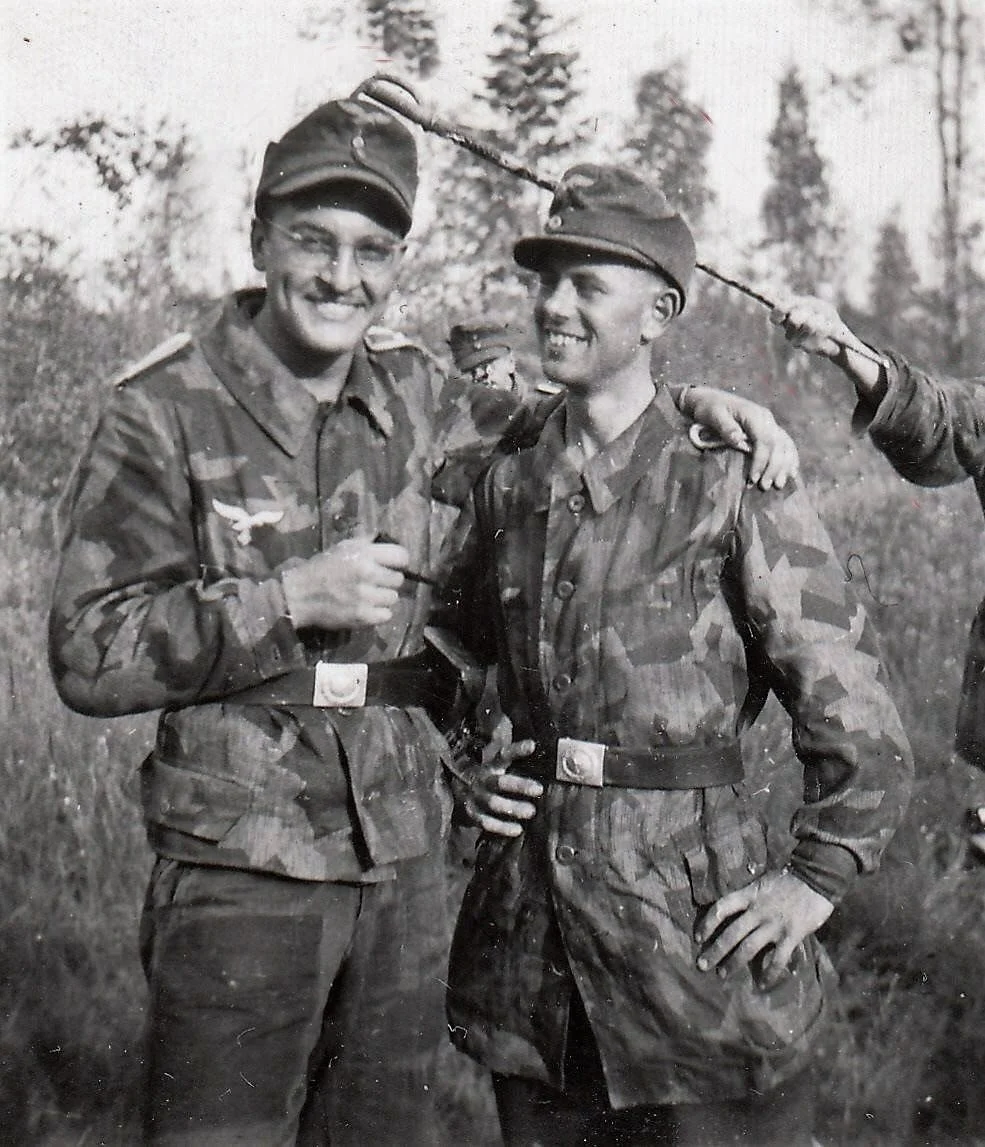
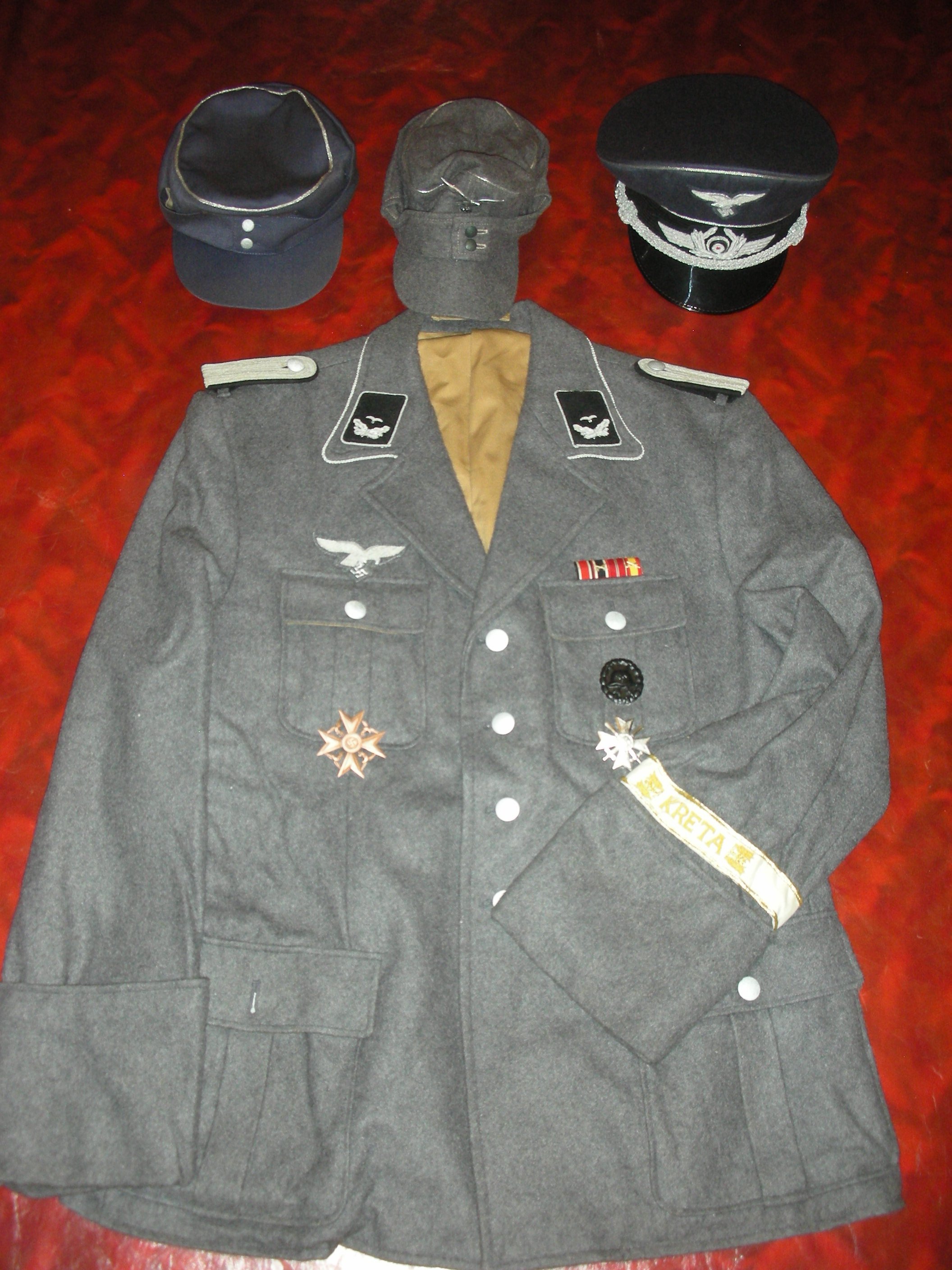
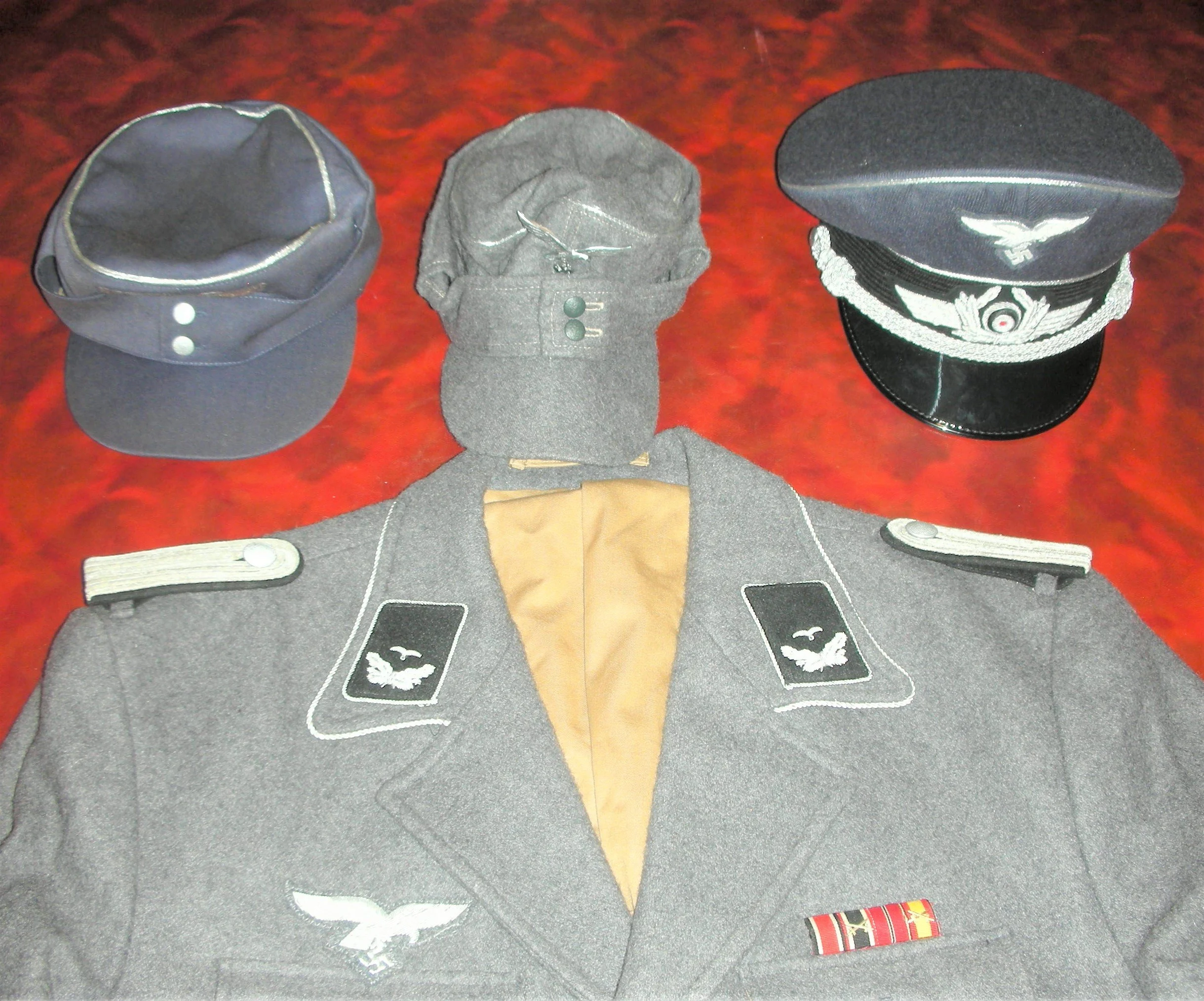
NEW Oberleutnant 9. Luftwaffe Jäger Regiment 5. Luftwafe Feld-Division:
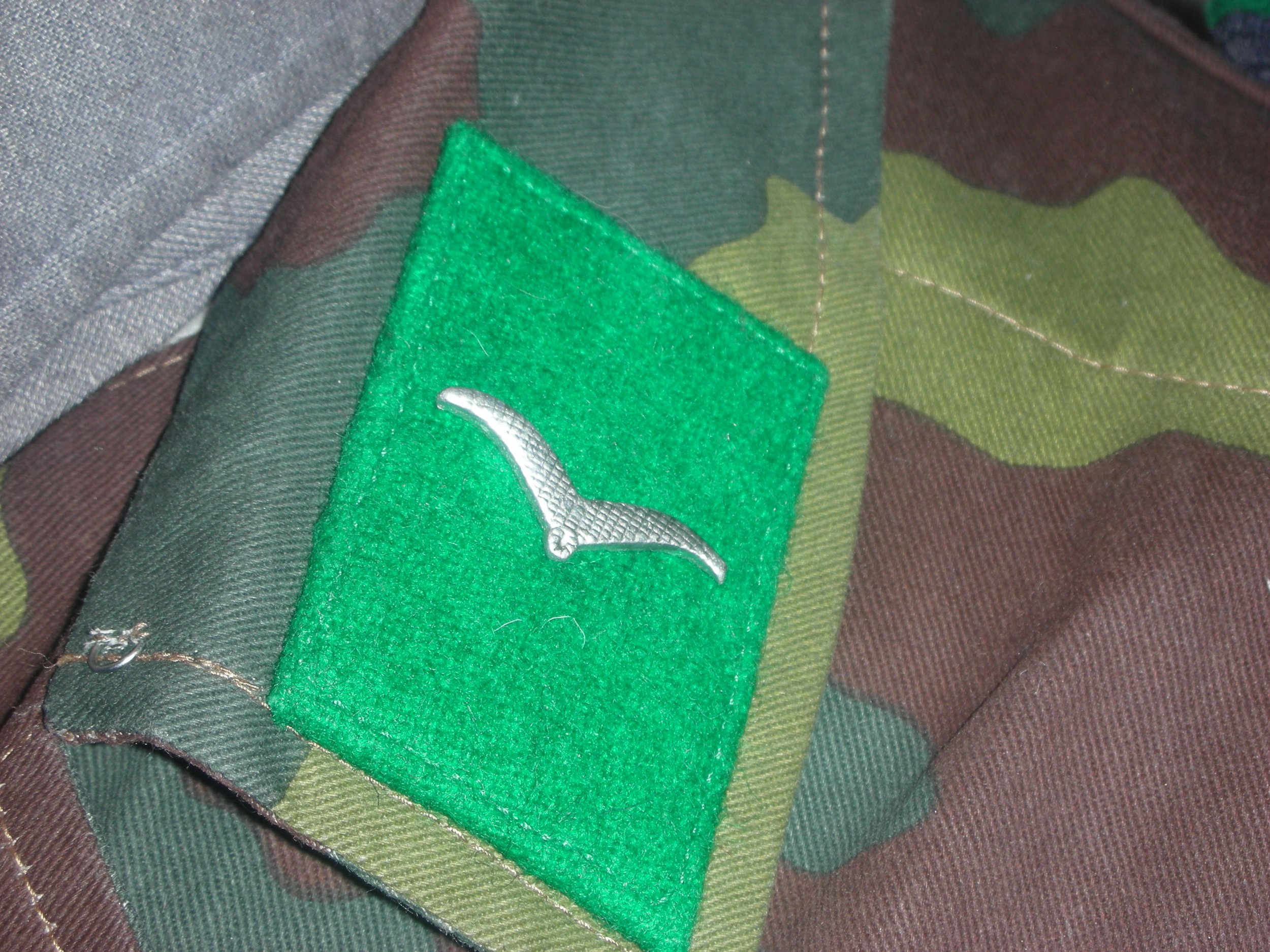
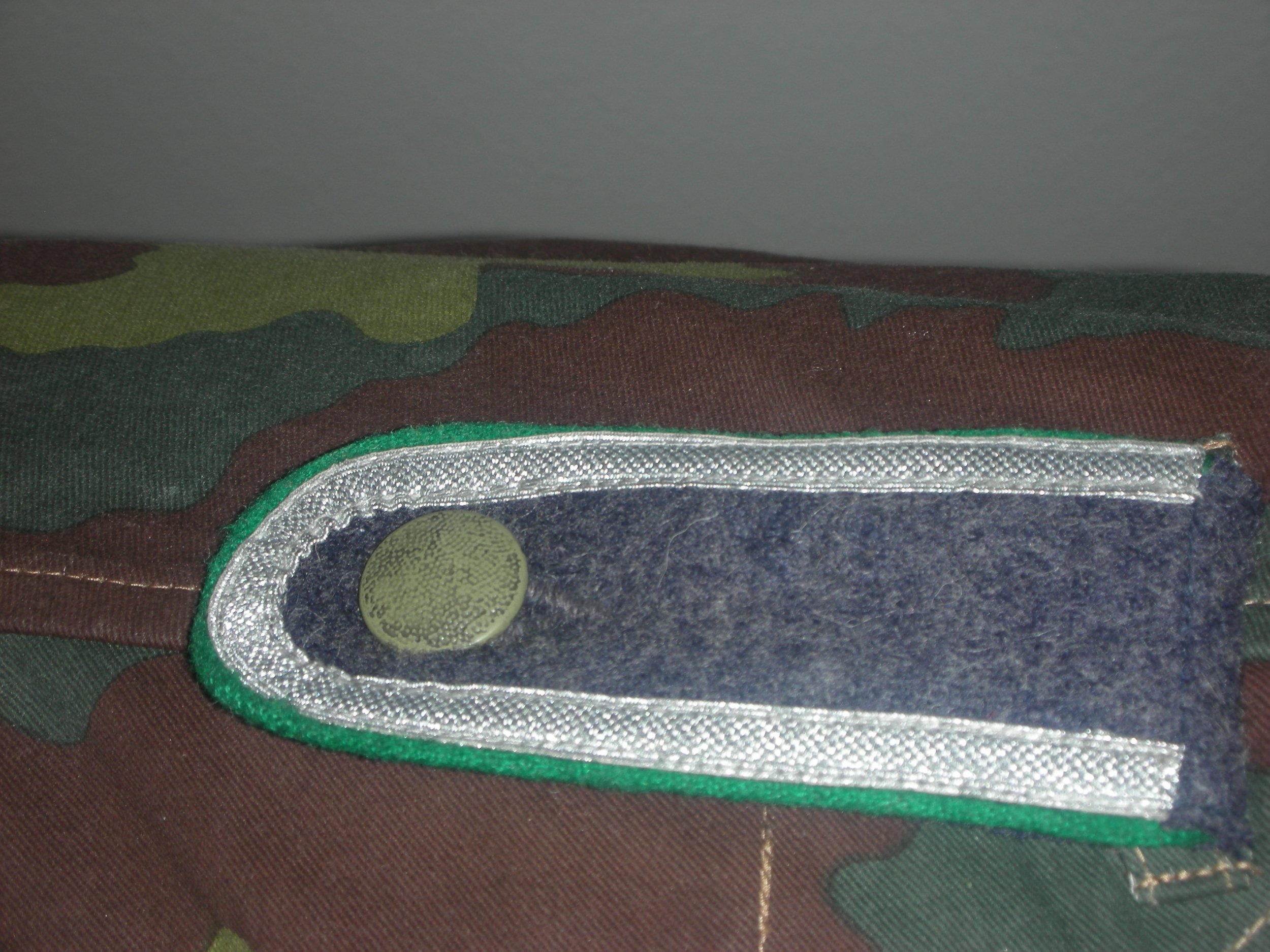
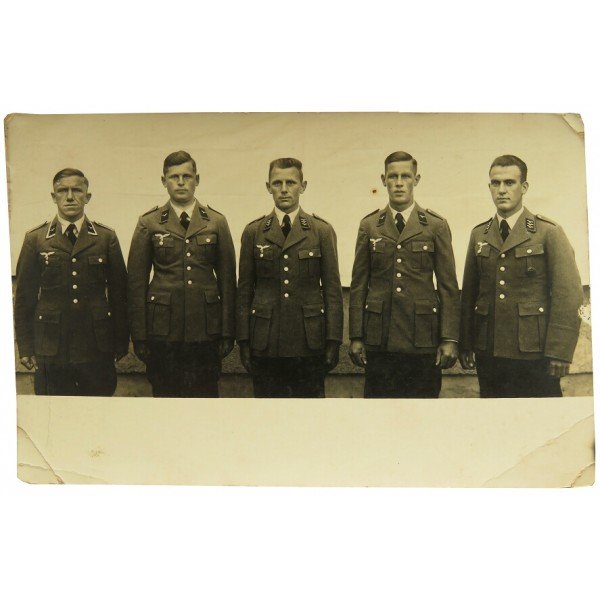
Since this was a come-as-you-are affair, senior NCOs and officers often wore the four-pocket Model 1935 Tuchock. They’re Litzen u. Schulterklappen showed the dunklegrun Waffen farben of the Feld Division. Shown are the main types of uniforms worn by the regimental soldiers.
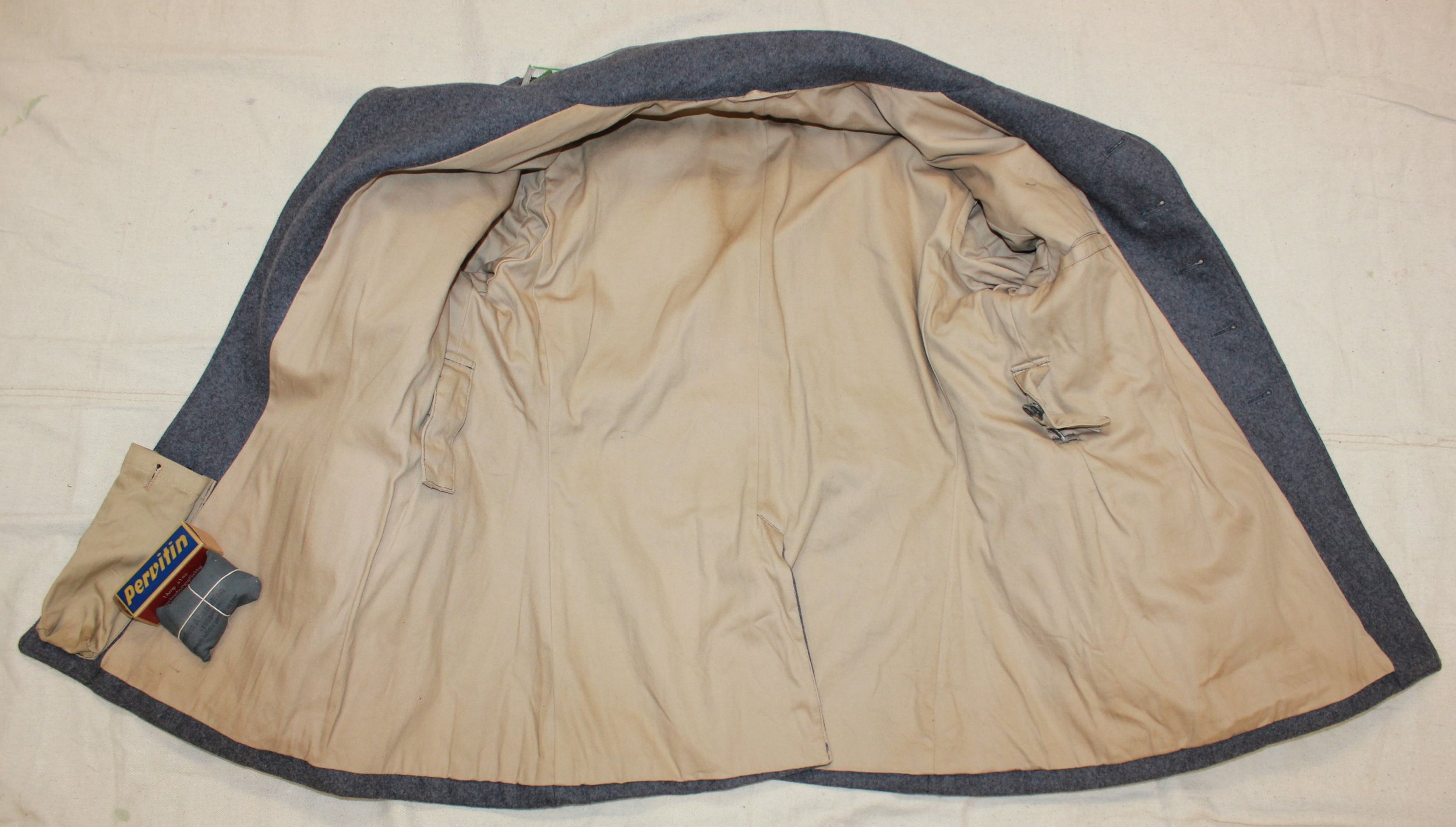
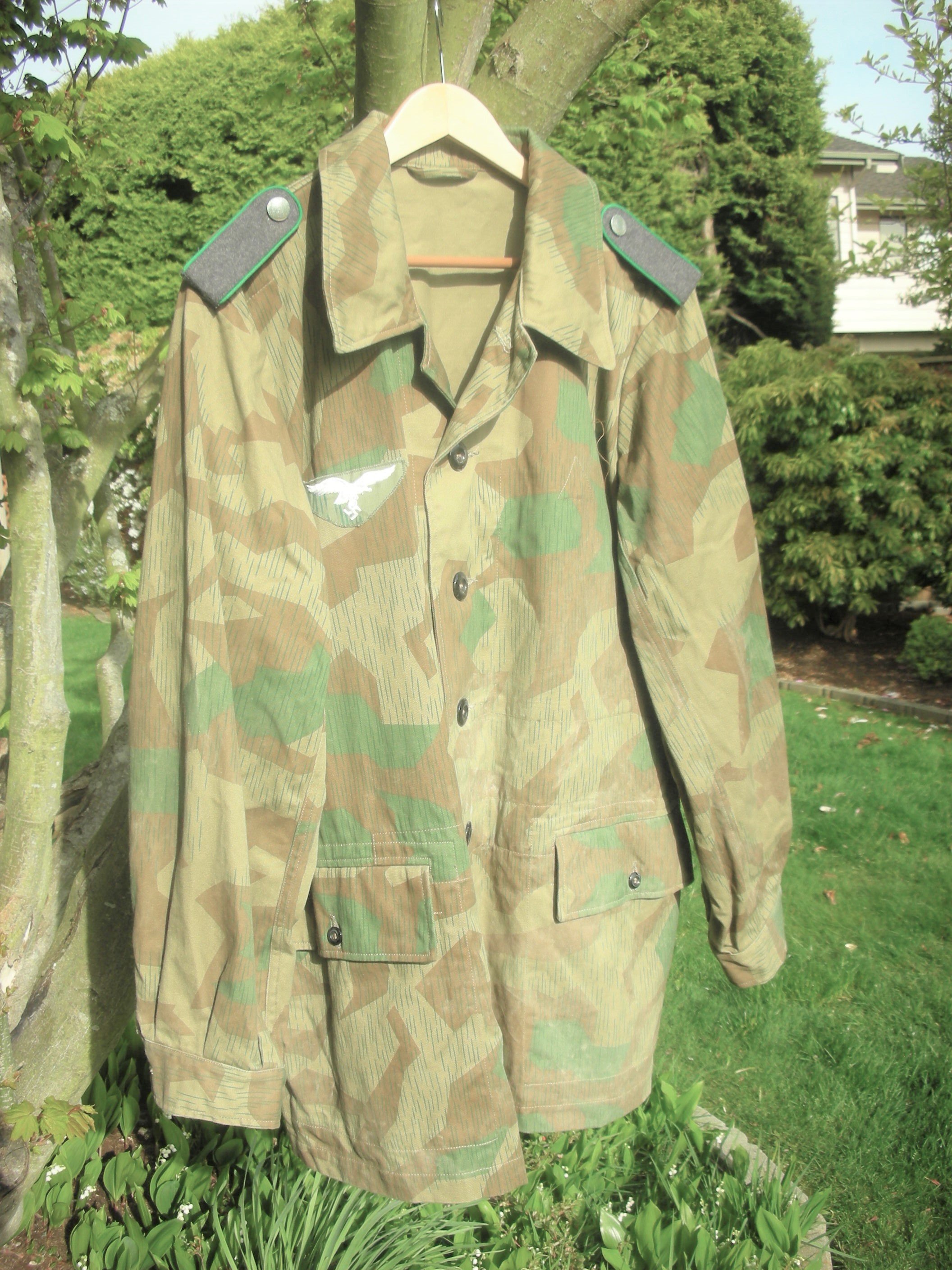
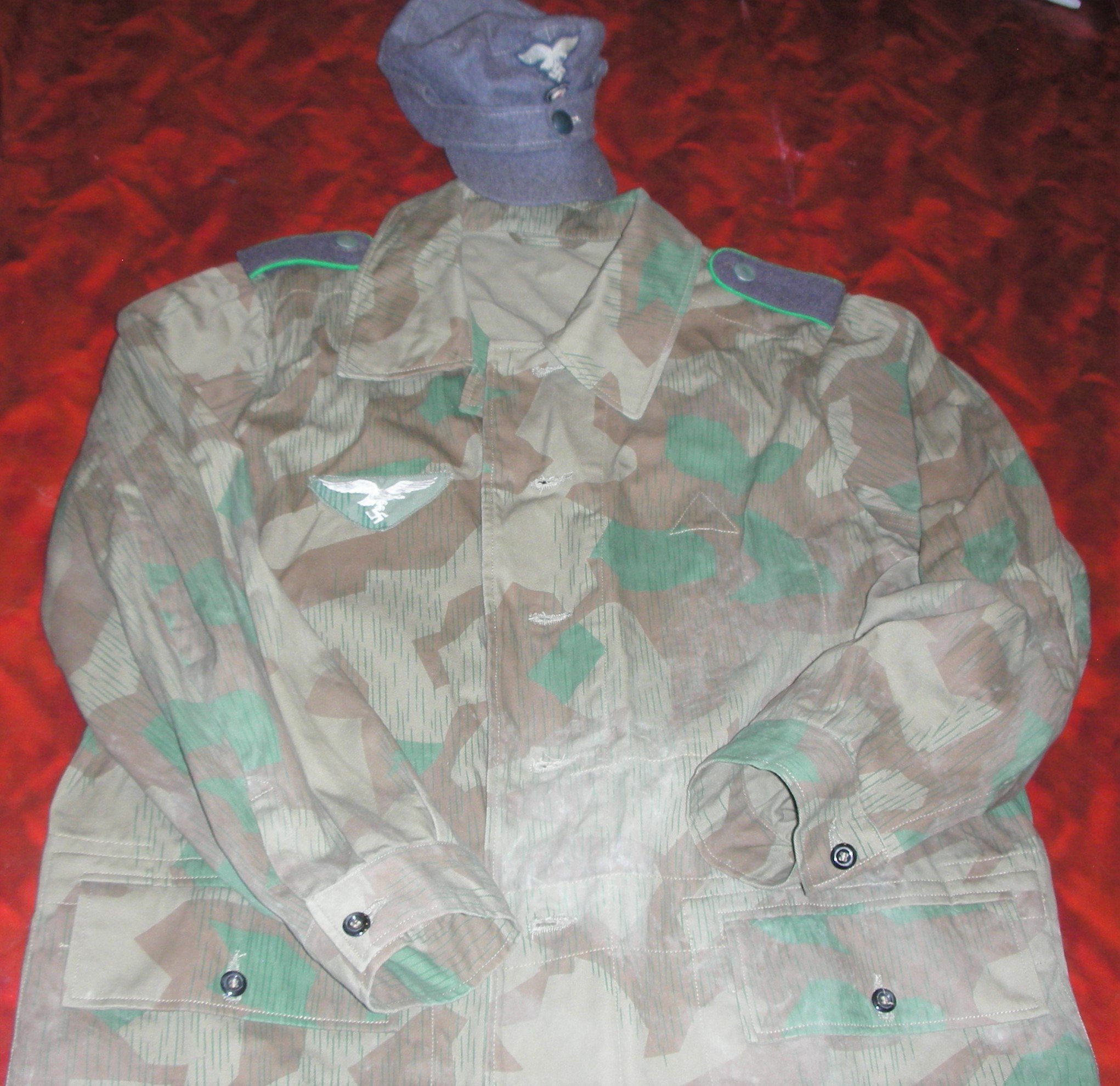
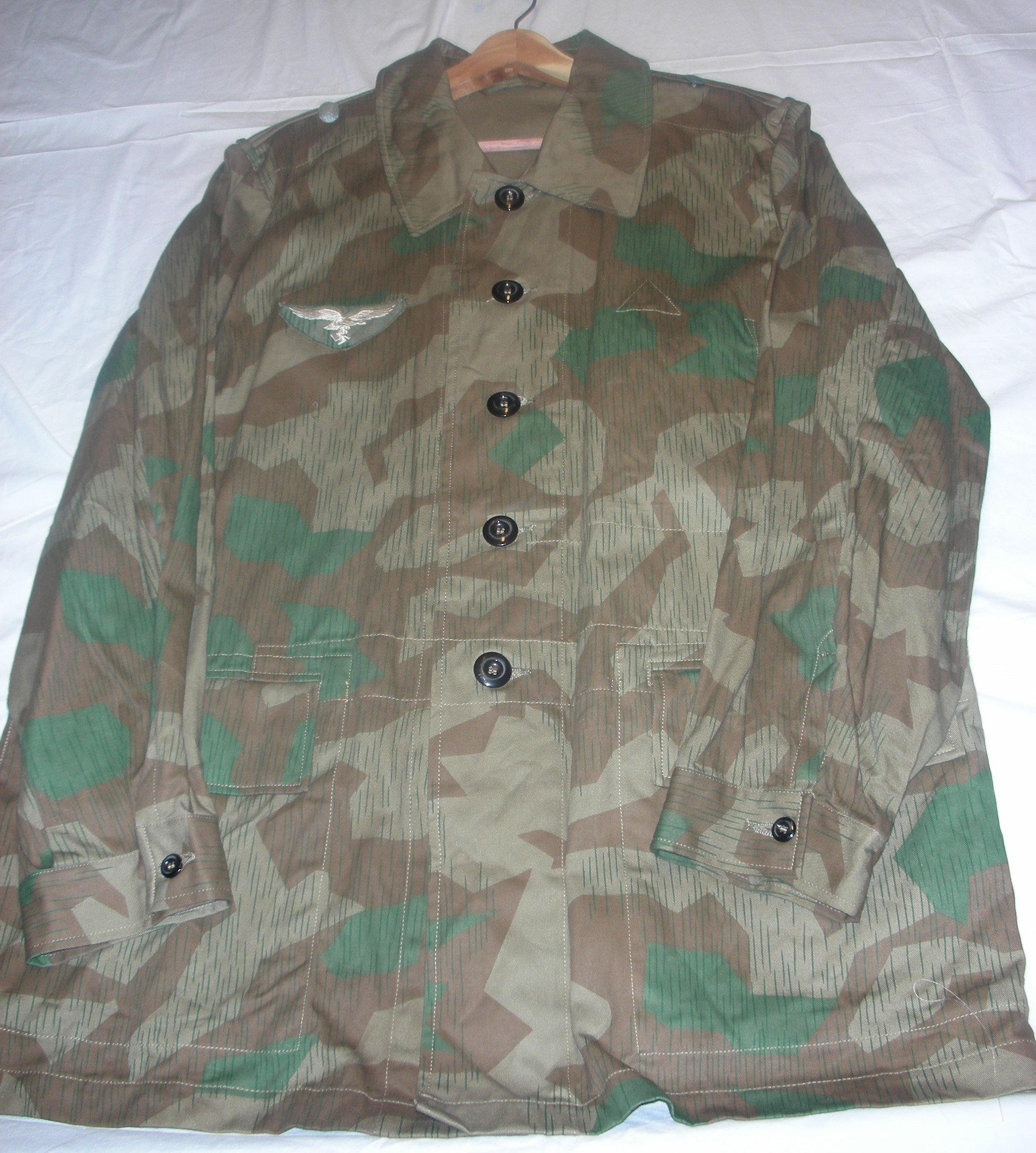
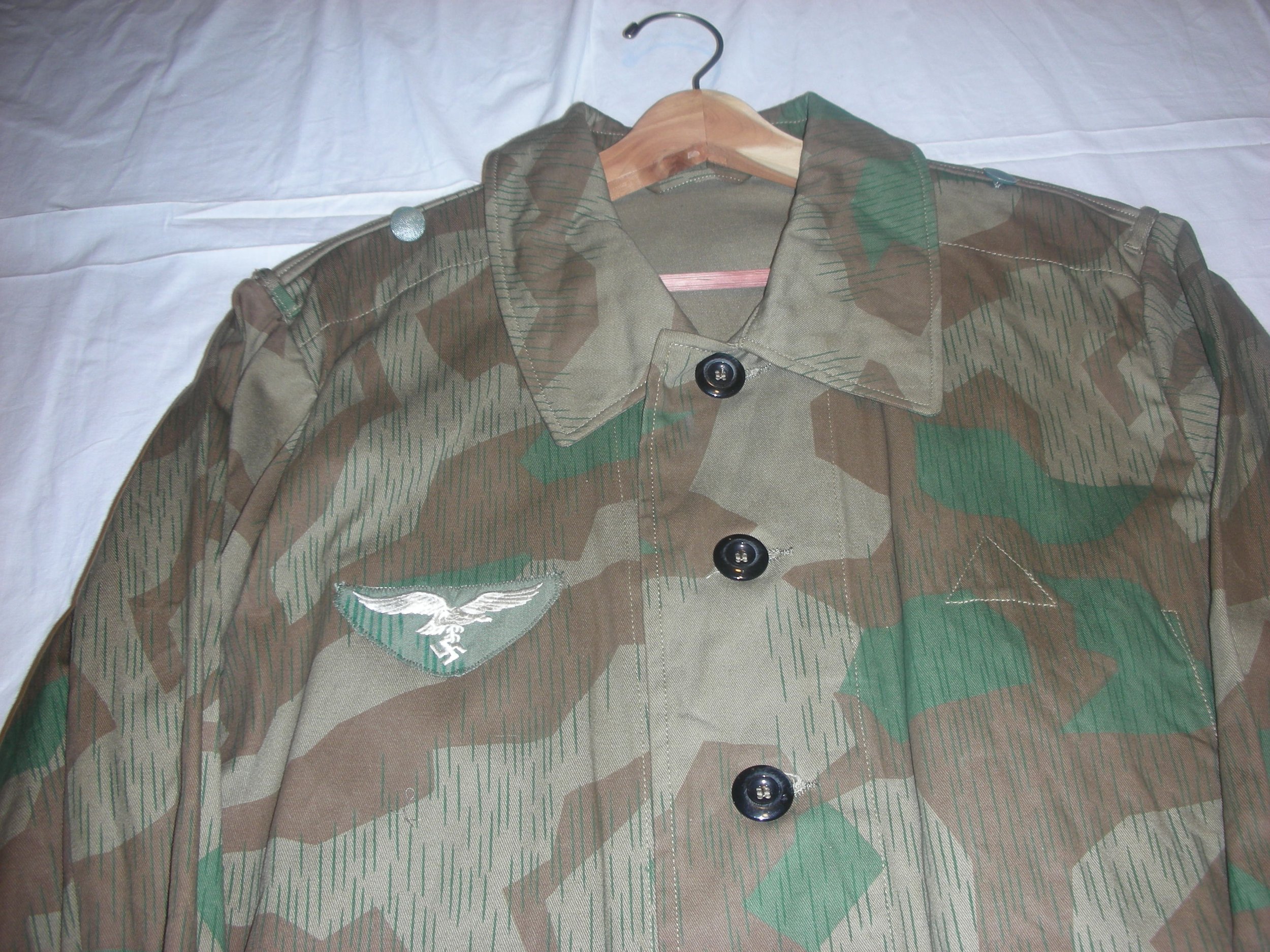
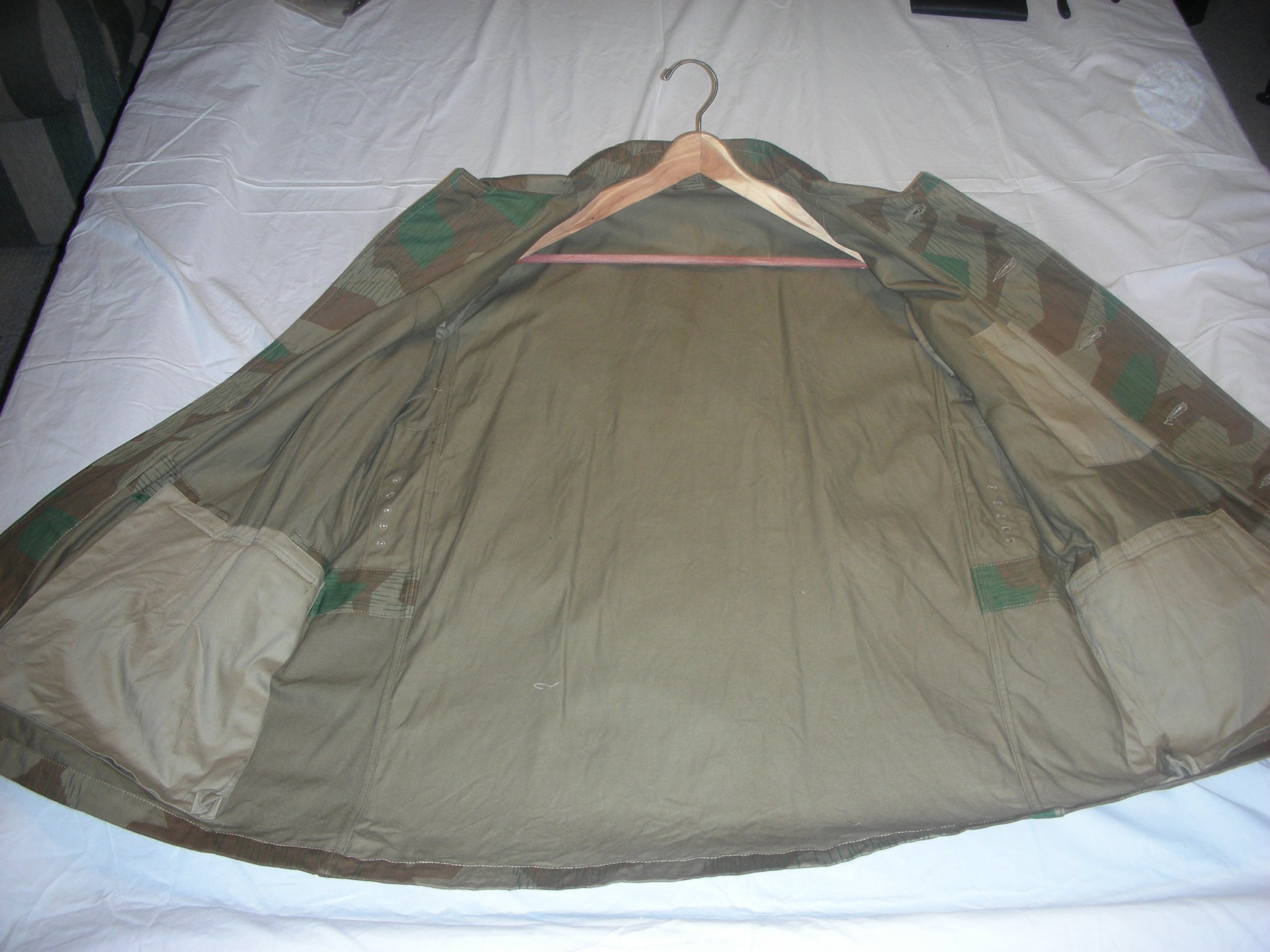
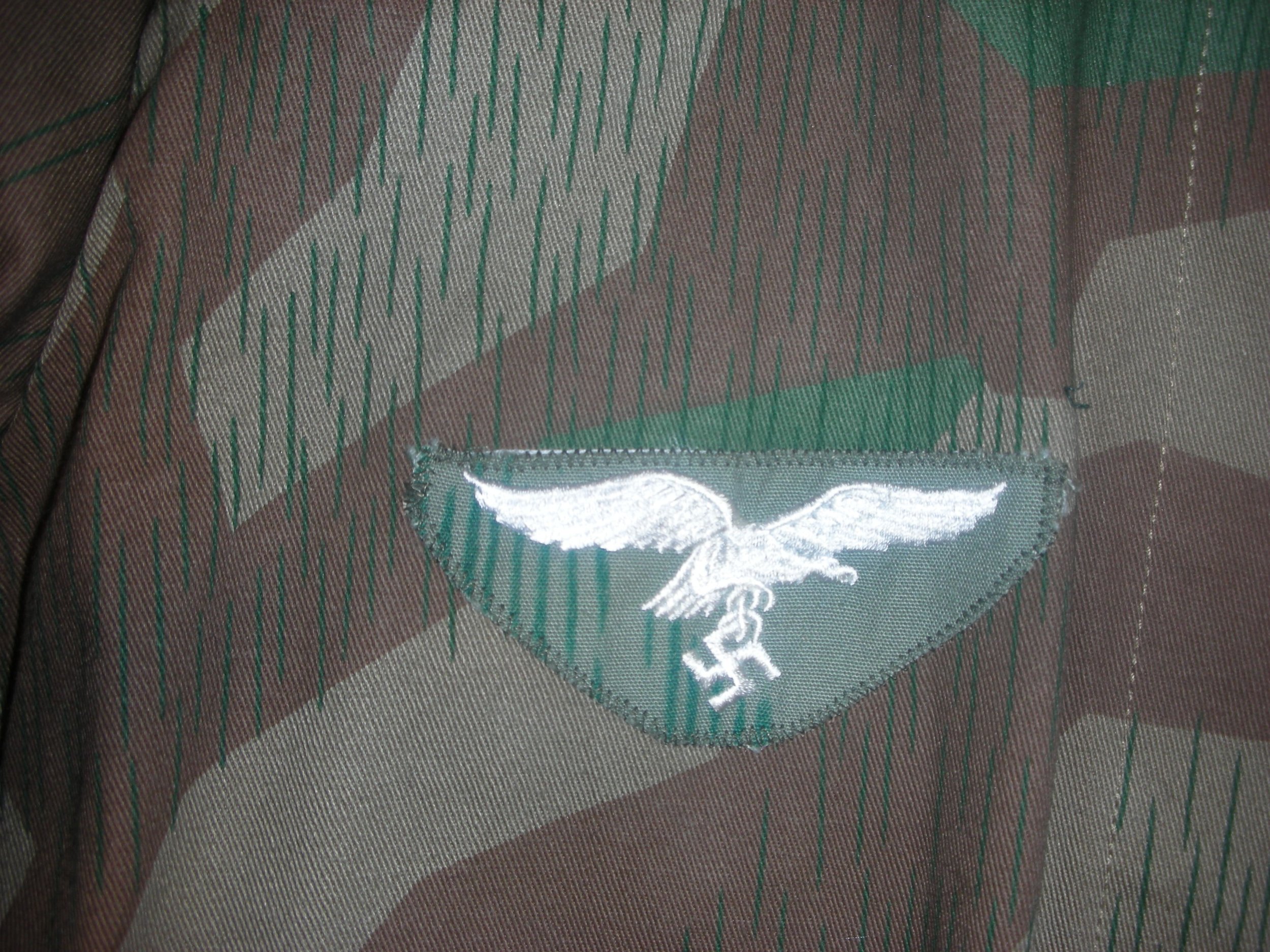
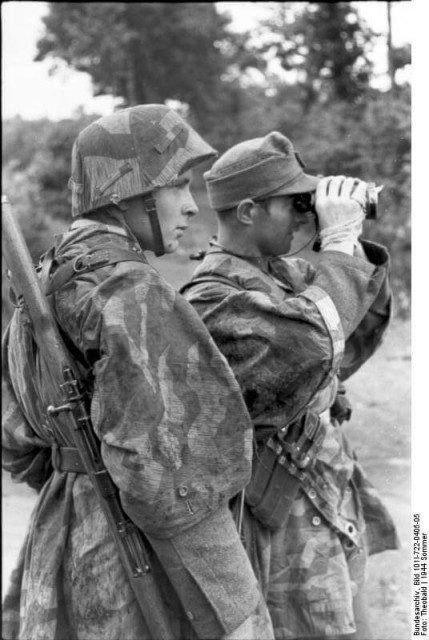
Luftwaffe Ground Forces 4-pocket Splinter Camouflaged Over-Jacket:
These would be, I think, the most common camouflaged jackets worn by the Luftwaffe Ground Forces, well, next to wearing a shelter quarter, like a rain poncho by the infantrymen, and Flak-Artillery Forces. I think also there were several variants of the over-jacket itself. The camouflaged overjacket could go with any of the Luftwaffe Infantry and Flak units shown in the collection.
*Obviously I need more pictures of this uniform.
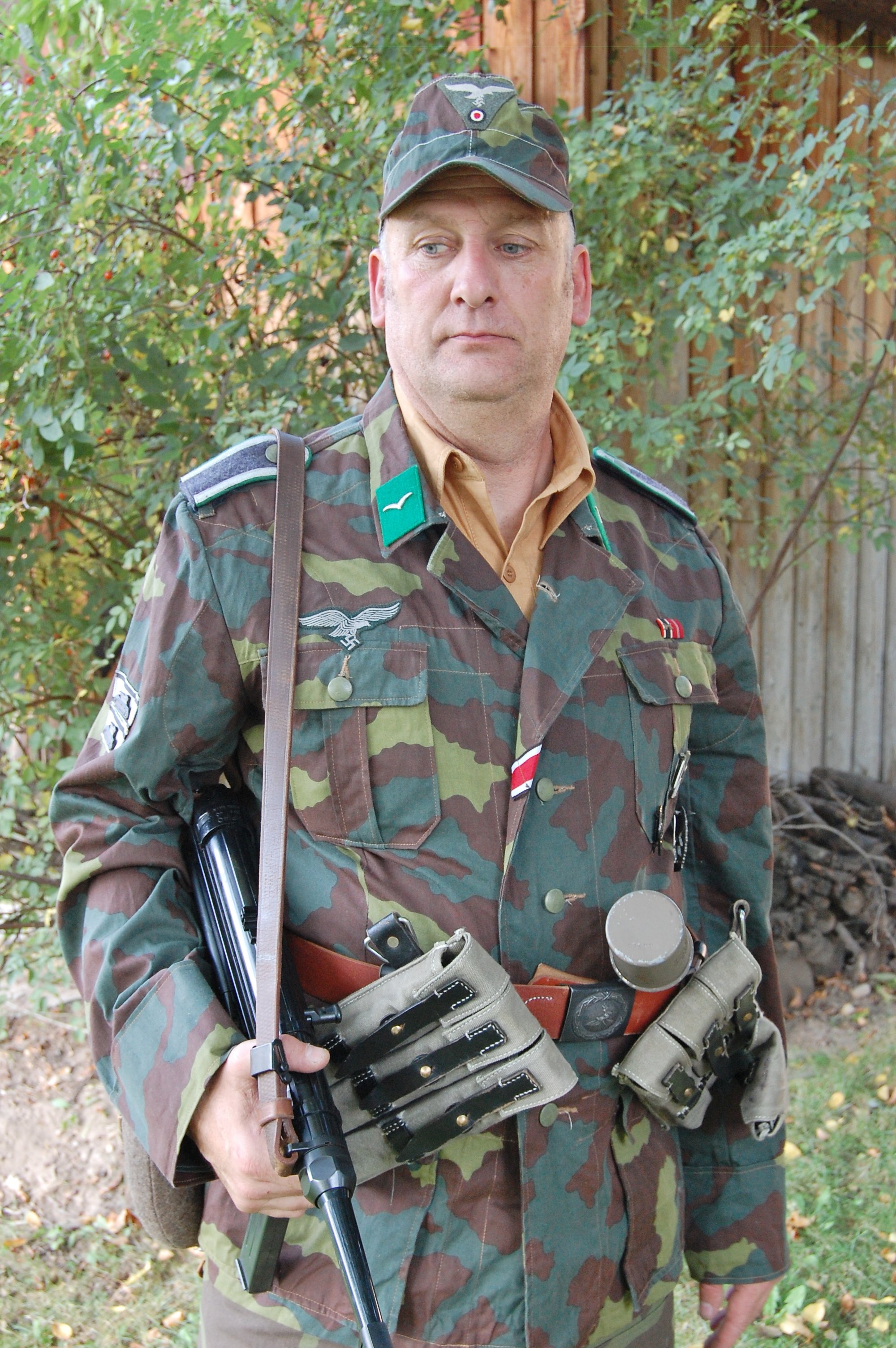
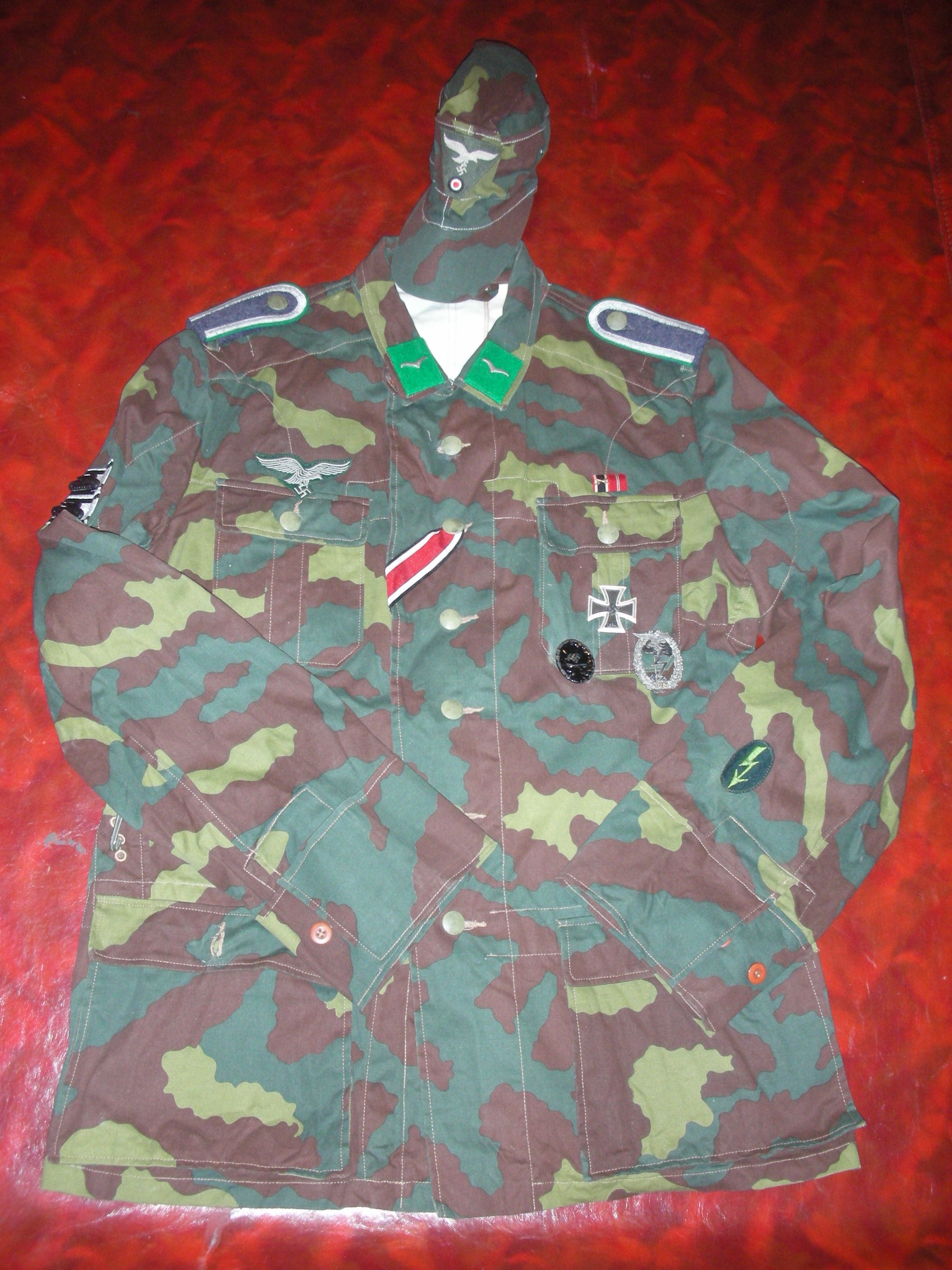
Unteroffizier, 39 Field Infantry Regiment. 20 Luftwaffe Field Division:
After being formed in 1943, the 20. Field Division transferred from Germany to Denmark in August of that year, where it remained until it transferred to combat duty in Italy in June 1944. After five months in combat, the division was reduced to a size where it was put under the command of the 26th Panzer Division until November, when it was taken off the line, and the remaining cadre was assigned to a training division, probably the 155th.
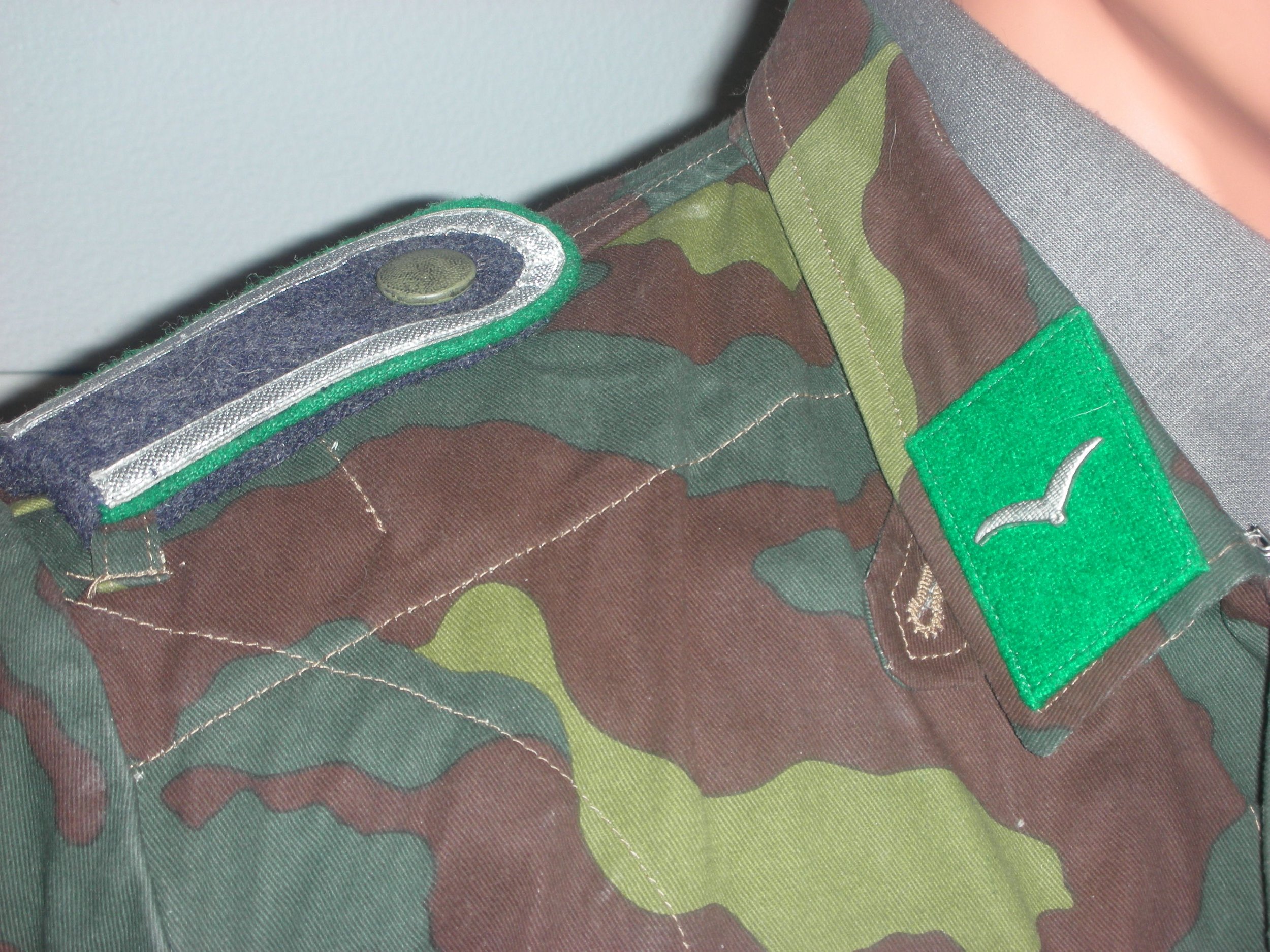
Lacking infantry combat leaders, Luftwaffe Field Divisions drew NCOs and Officers from the Army. Wearing their Heer uniforms alongside their Luftwaffe troop,s these men may have found reason to adapt to a form of Luftwaffe dress that would make them closer to their men. The collar tab change may have been changed from the Heer style as well, to clarify his rank.
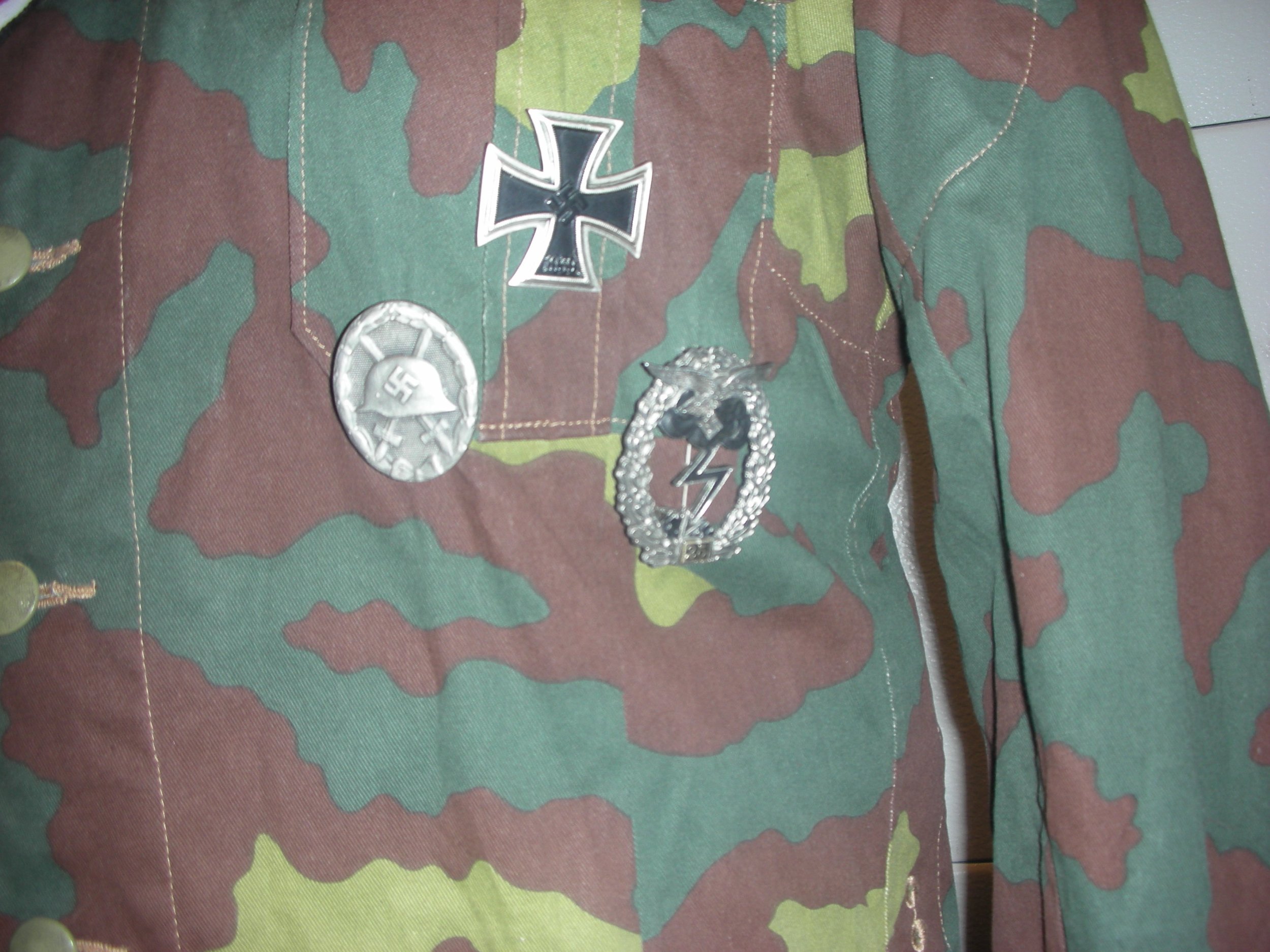
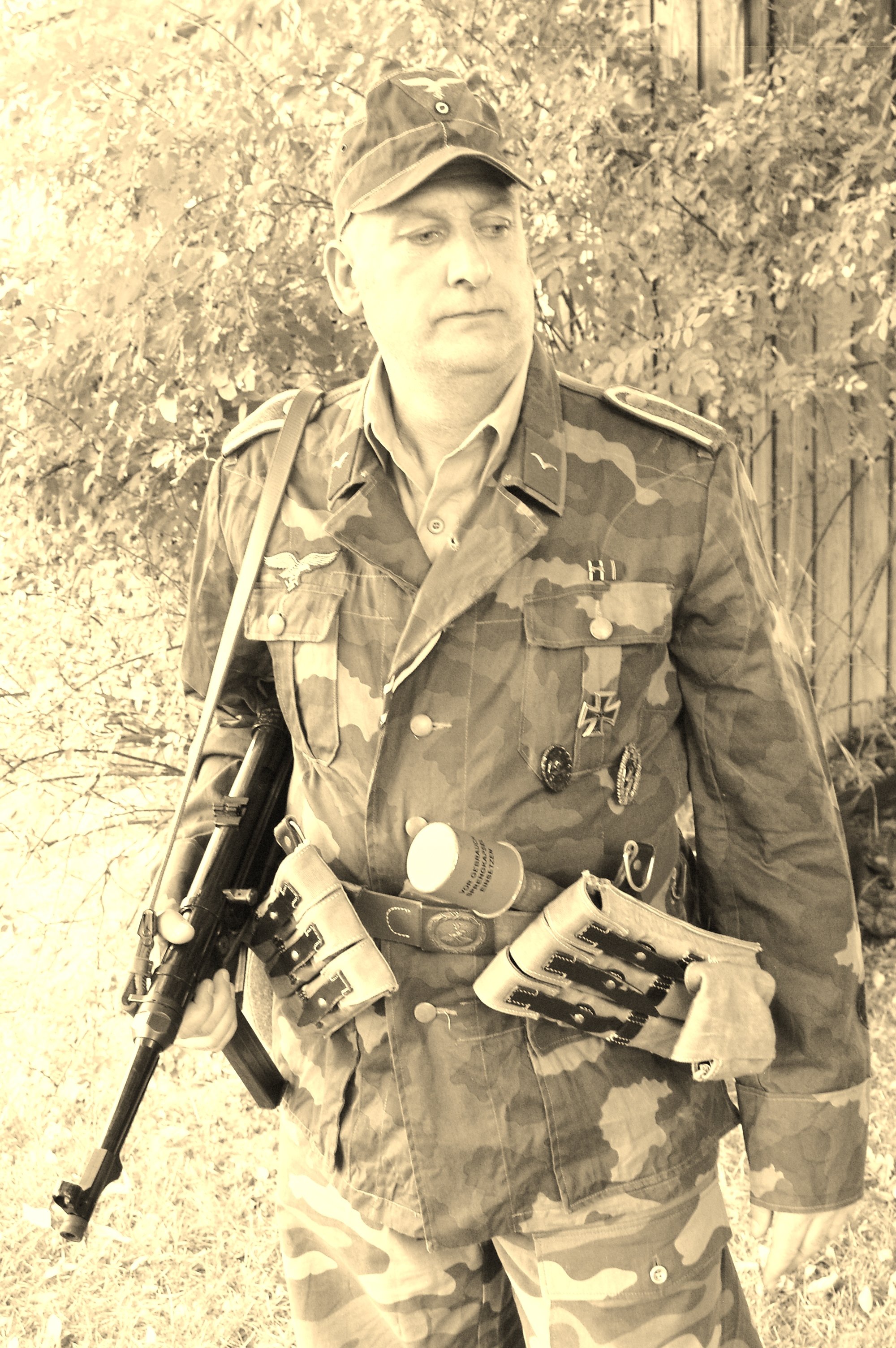
This is the case with this Unteroffizier who has replaced his worn-out wool-Heer green uniform tunic with local Italian camouflage material, cut in what was thought to be the Luftwaffe cut. A communication expert, and assigned, he wears the ‘Funker’ blitz on his sleeve, but like his tabs and boards, has the green on them for the Luftwaffe Ground Troops.
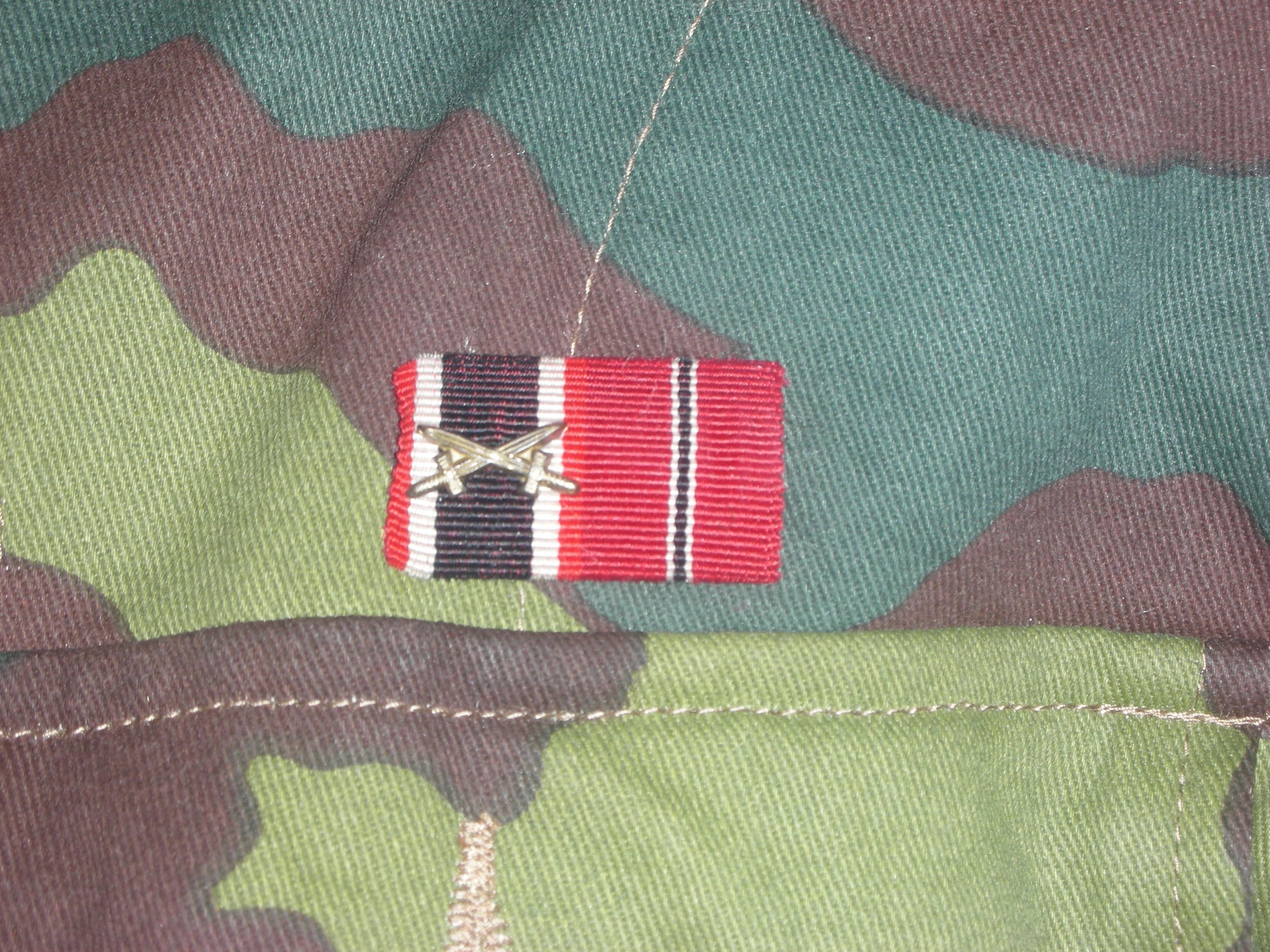
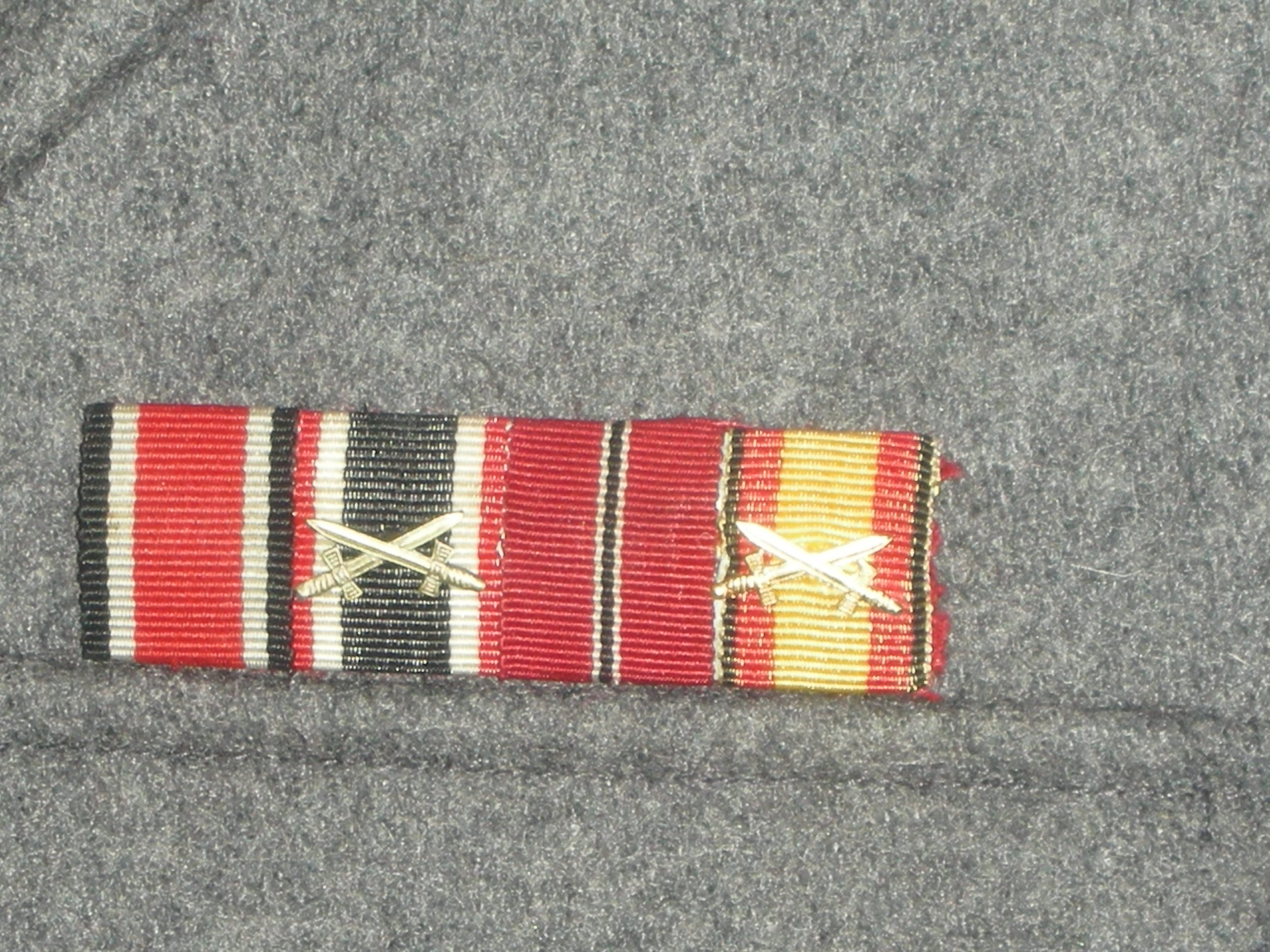
For the photo shoot, he got assigned an MP-40 machine pistol and the ammo pouches to go with it, on his leather belt, fewer Y-straps, and in the belt he placed some stick grenades. The uniform carries the Luftwaffe pattern National Eagle as well, on a rare green backing. He has been around, and on the ribbons bar, has the Eastern Front Ribbon, as well as the War Merit Cross with Swords, from prior service. Also for his leadership, he has earned the Iron Cross 1st Class Meadly hanging from loops, and the II class in the buttonhole.
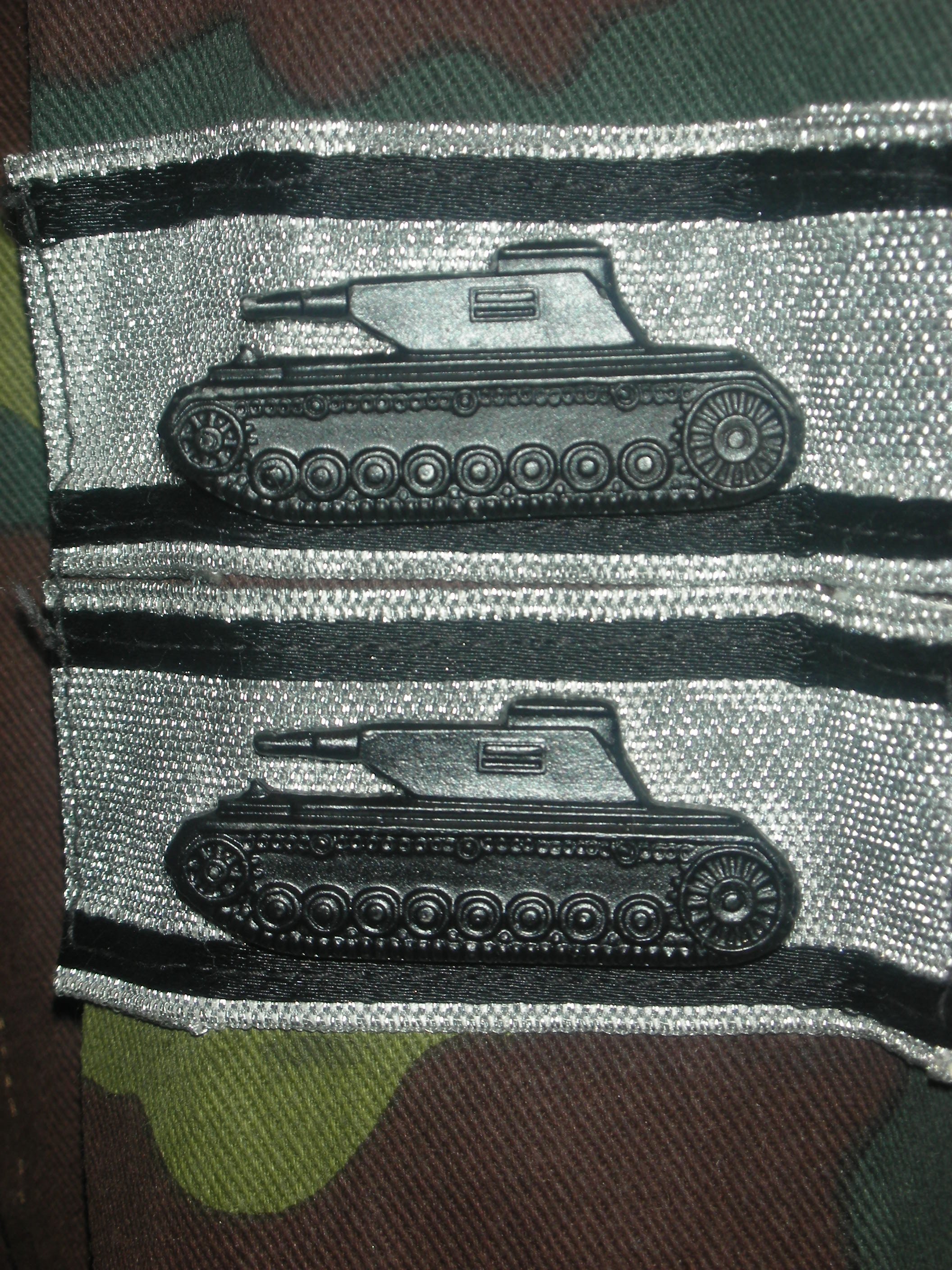
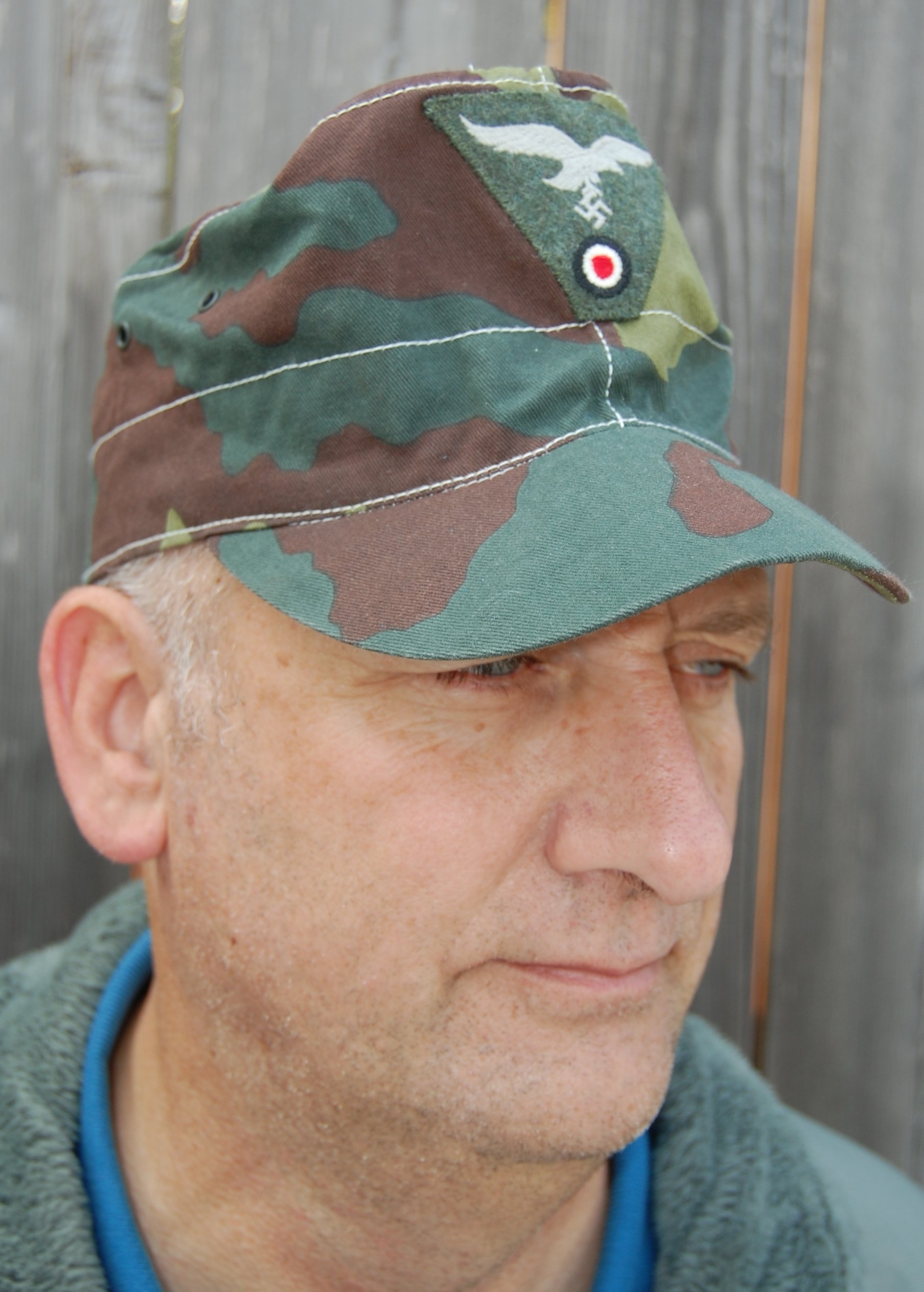
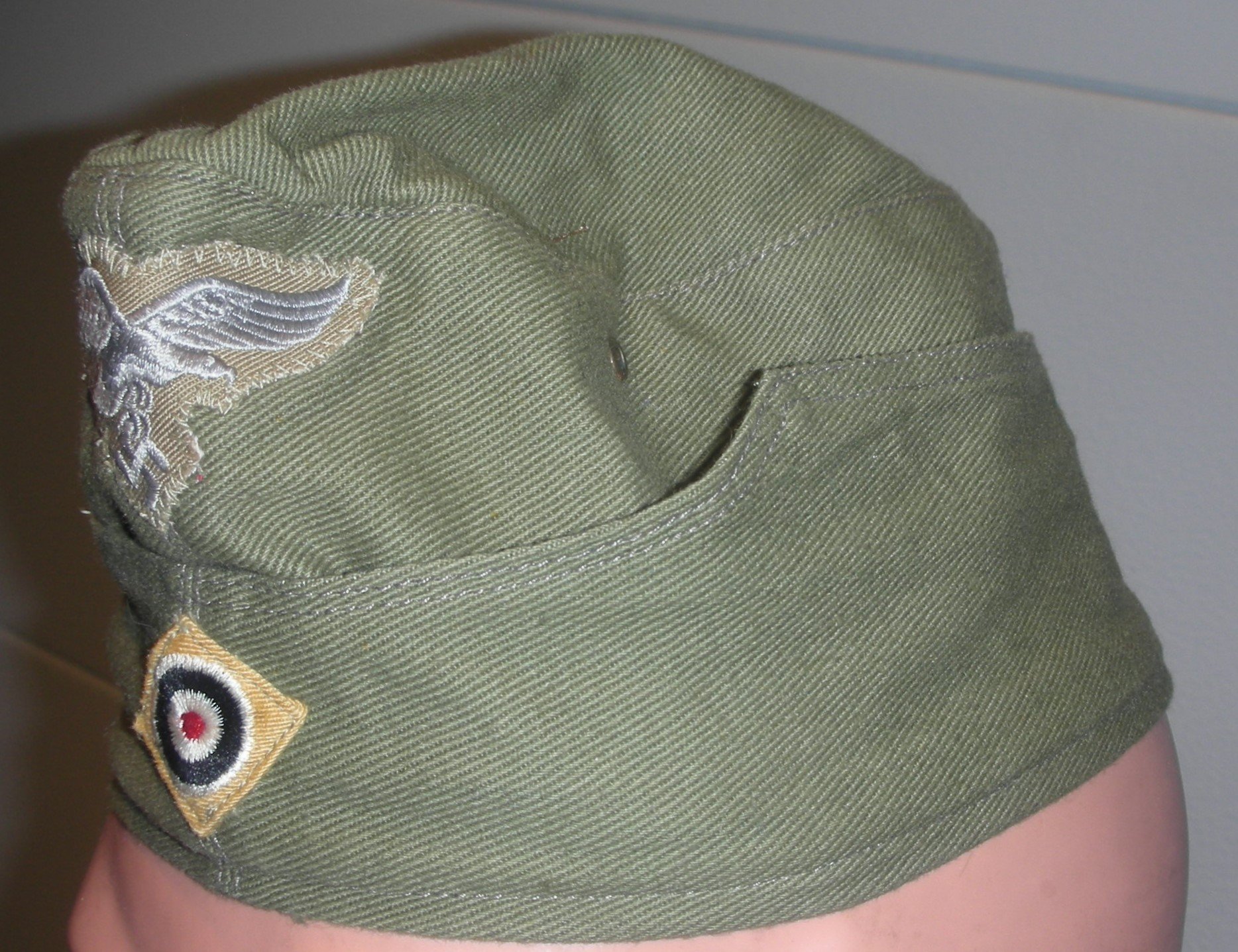
Also on the left pocket hangs the Silver Wound Badge and the rare Luftwaffe Ground Assault Badge. Also, he’s recognized to have knocked out several enemy tanks single-handedly, as seen by the decorations on the right sleeve. With the uniform, he likely would have a helmet, but these were seen less and less in the last year of the war. I have an overseas cap, a Tropical cap, as well as a matching camouflage pattern M42 style hat with the uniform.
LW. Reversible Winter Over-jacket:
I’ve misplaced the story for this, but in short, it’s the Luftwaffe’s version of the ‘Freezer-Suit’ reversible and insulated they were a lot of work, and in the field, they were scarce, all winter uniforms through the war for the Germans, were in short supply, never enough, and rarely issued to the troops, they grabbed what they could, when they could, the moment stock showed up-it was divvied out. I imagine many ended up with the Heer pattern over-suits!
It’s the ‘Mouse-Gray’ color and white on the other, he carries on the forearms pin-on yellow bands, as a code for the day, or what have you. His helmet is a bluer/gray color rather than feldgrau and retains its decals.
The uniform was used with all the field units, infantry, and artillery, ground crews for the aircraft, authorized for freezing conditions; they were seen mostly with those fighting in the east.
Luftwaffe Custom Winter cap:
A smaller size (approx. 56) made of sheep skin, for a warm winter cap. I have forgotten now what uniform this originally went with; it’s a nice cap, and fits with all the Luftwaffe uniforms that were worn in winter. Some uniforms shown here would have been worn under a winter jacket, which many troops acquired one way or another, from Russian Homes, etc. It could have been an Air crewman from the field forces, flak, panzer, or infantry.
*LW. Pioneer Company, Officer:
*I must dig up the story on this fellow, and it deserves new pictures.
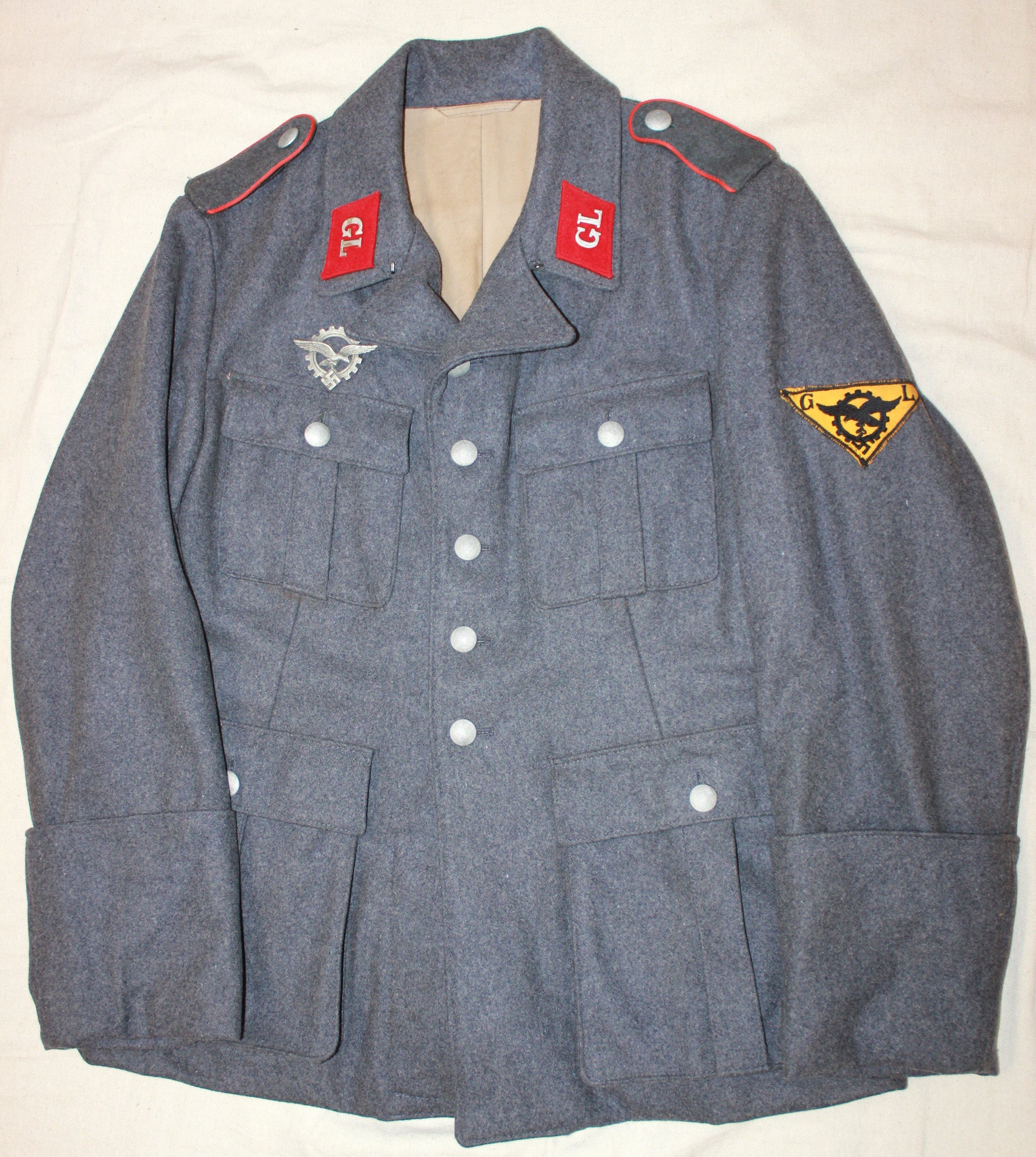
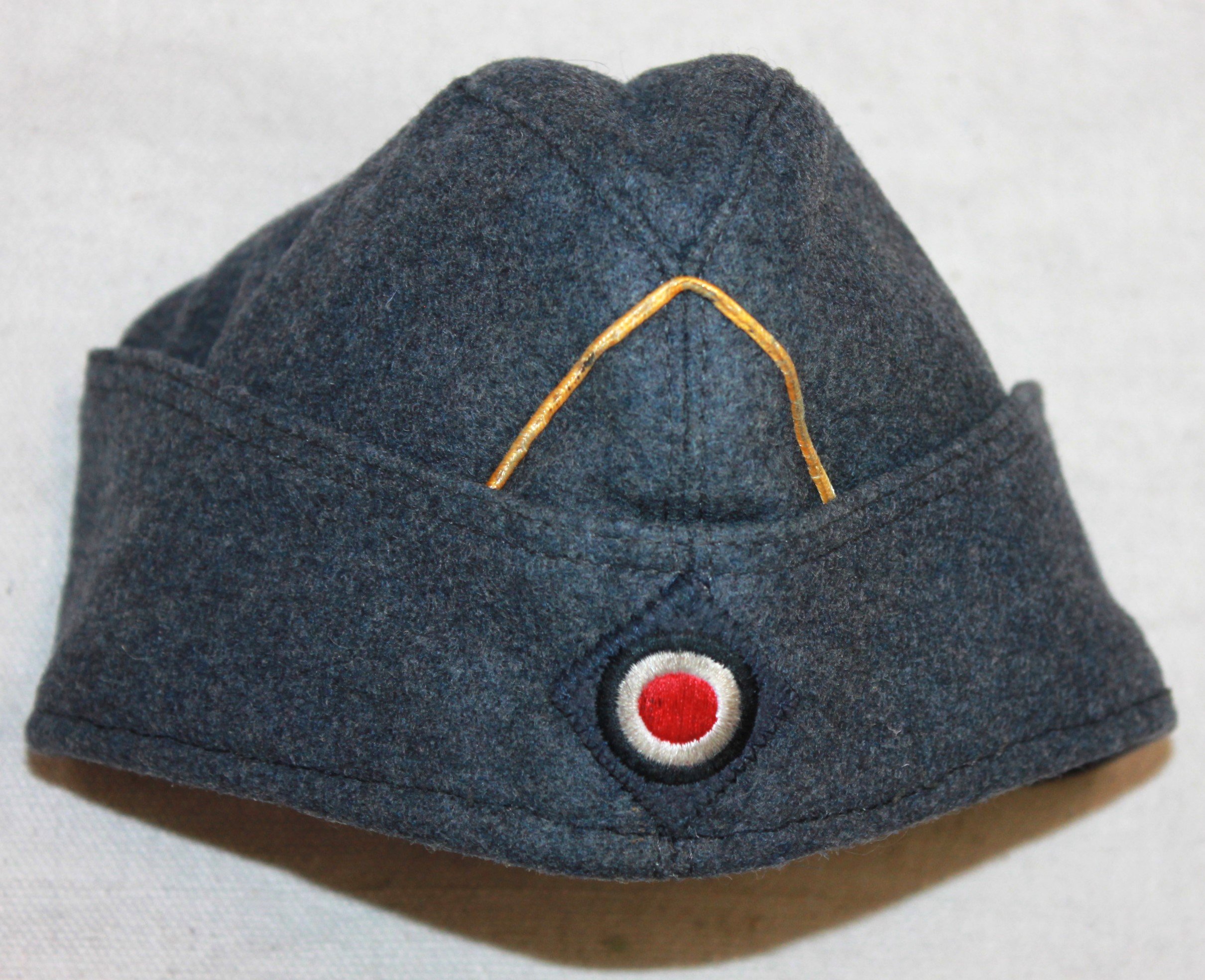
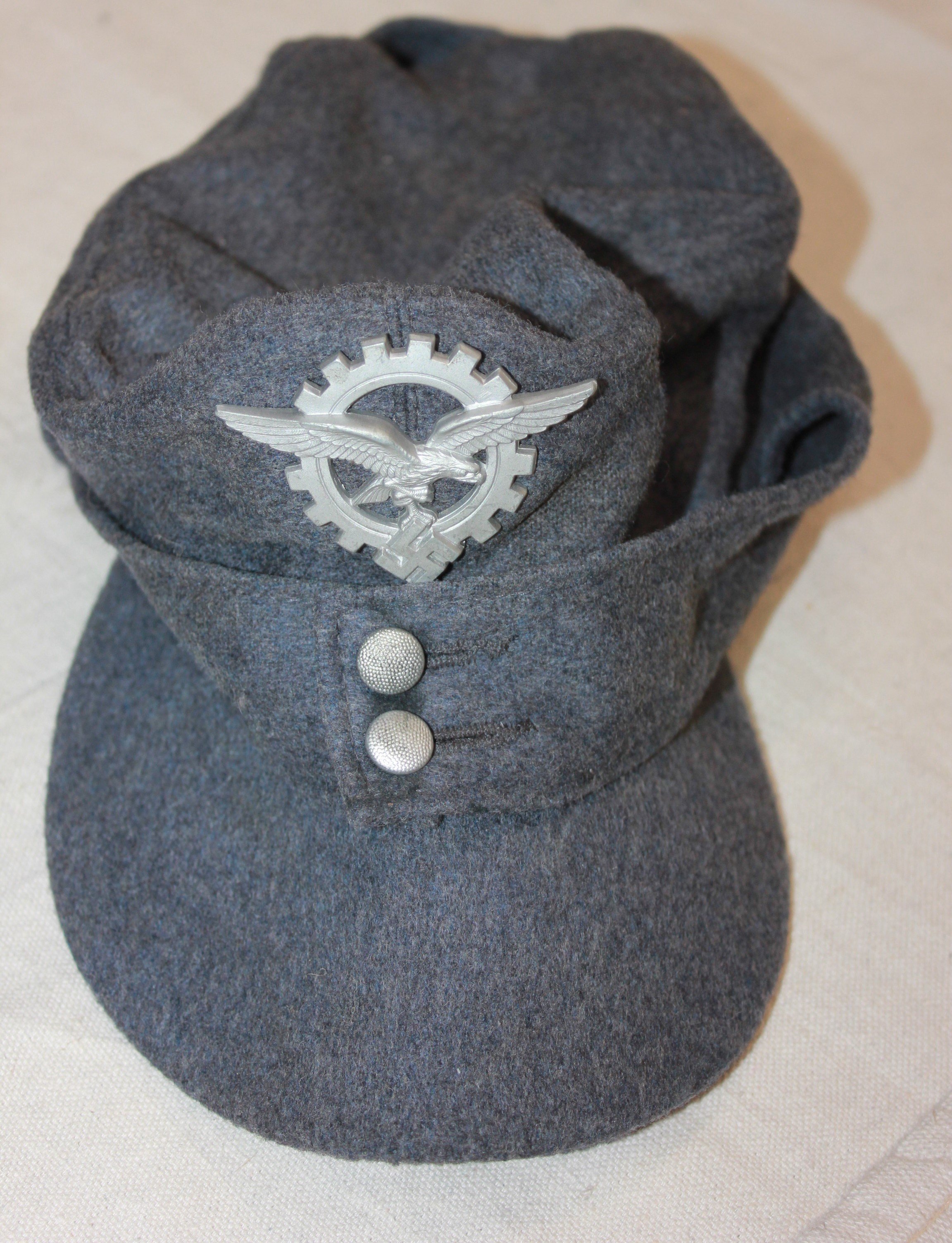
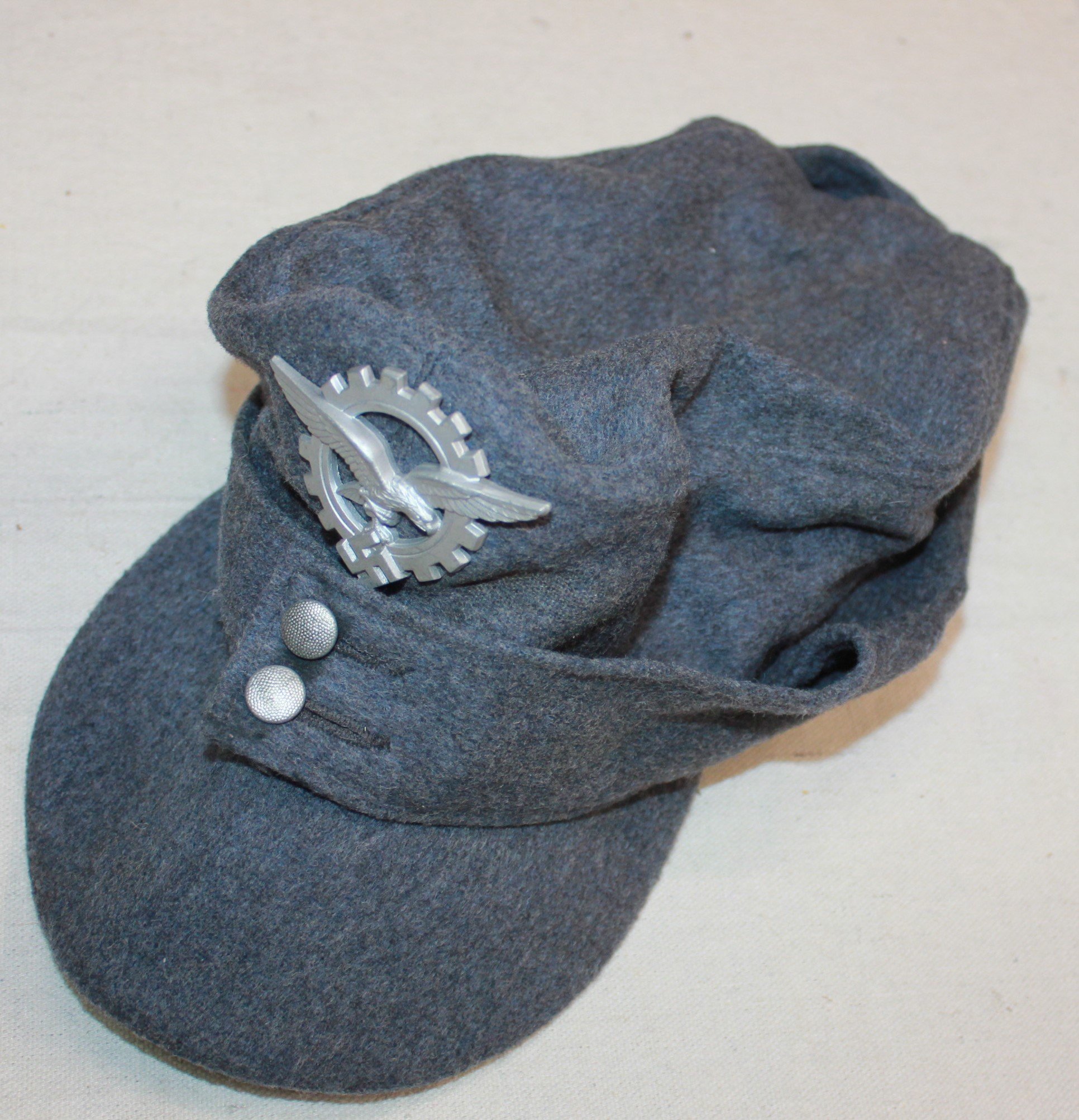
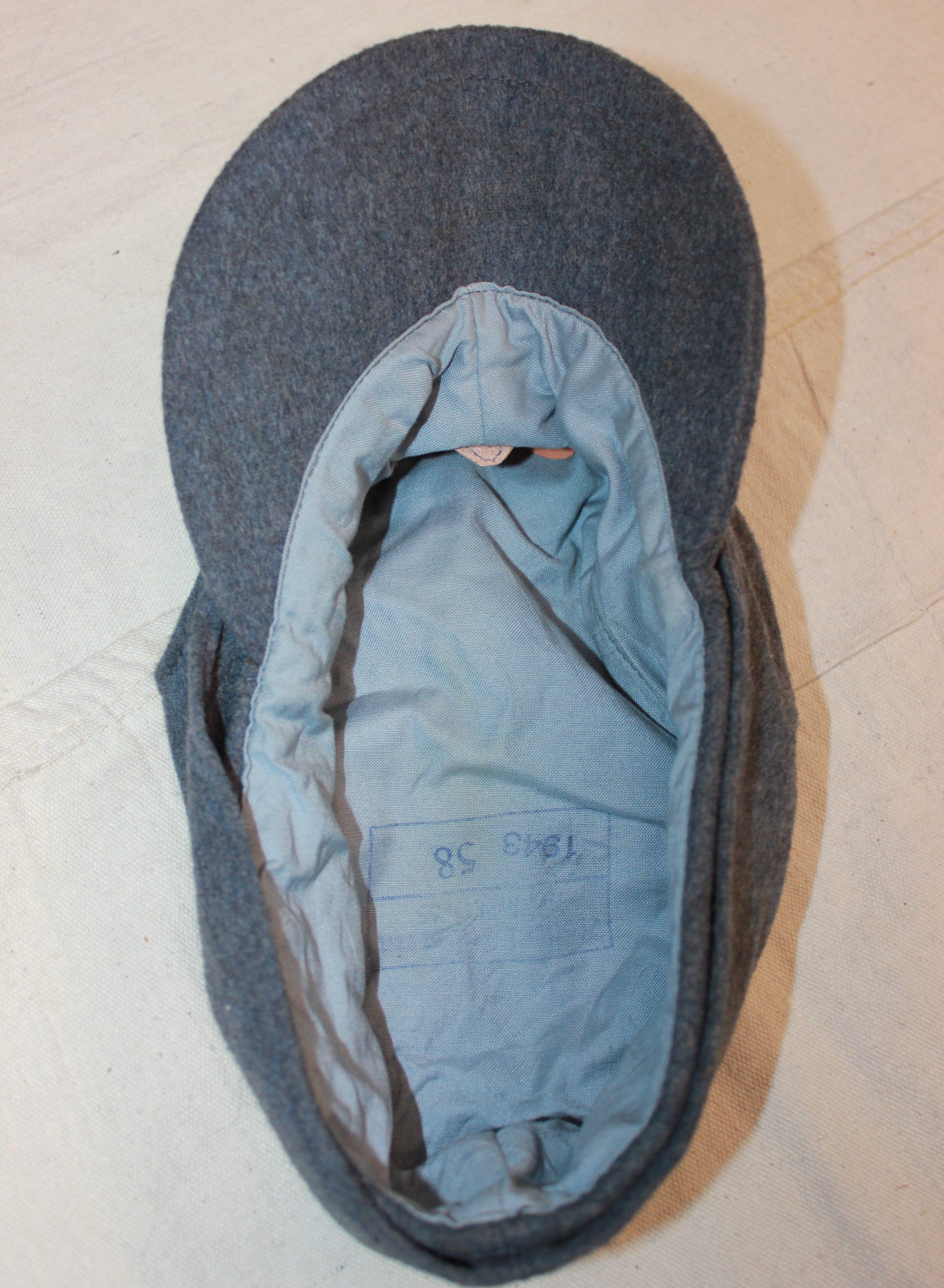
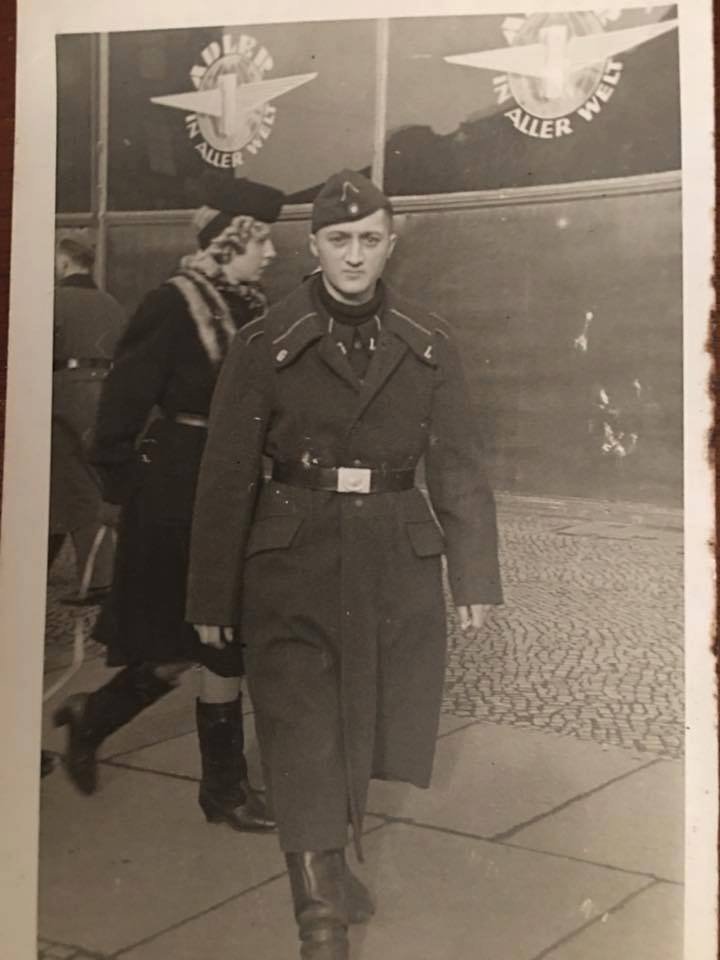
General Luftzeugmeister Techniker Fliegerkorps IX Niederland:
The Generalluftzeugmeister was a special organization made up of civil engineers working on Luftwaffe projects. They worked with and under Luftwaffe Officers and Senior NCOs at factories producing Luftwaffe armaments as well as in the field where Luftwaffe troops needed additional support with equipment.
Established in Februar 1939 under Generaloberst Ernst Udet until November 1941, when a command was assumed by Feldmarschall Erhard Milch. In 1944, it became part of the General Luftzeugmeister-Amt (Department of the Chief of Aircraft Procurement and Supply).
The main tasks of the Generalluftzeugmeister included the development, testing, and procurement of all material for the German Luftwaffe during World War II, as well as the provision of supplies for all the Luftwaffe's subordinate offices.
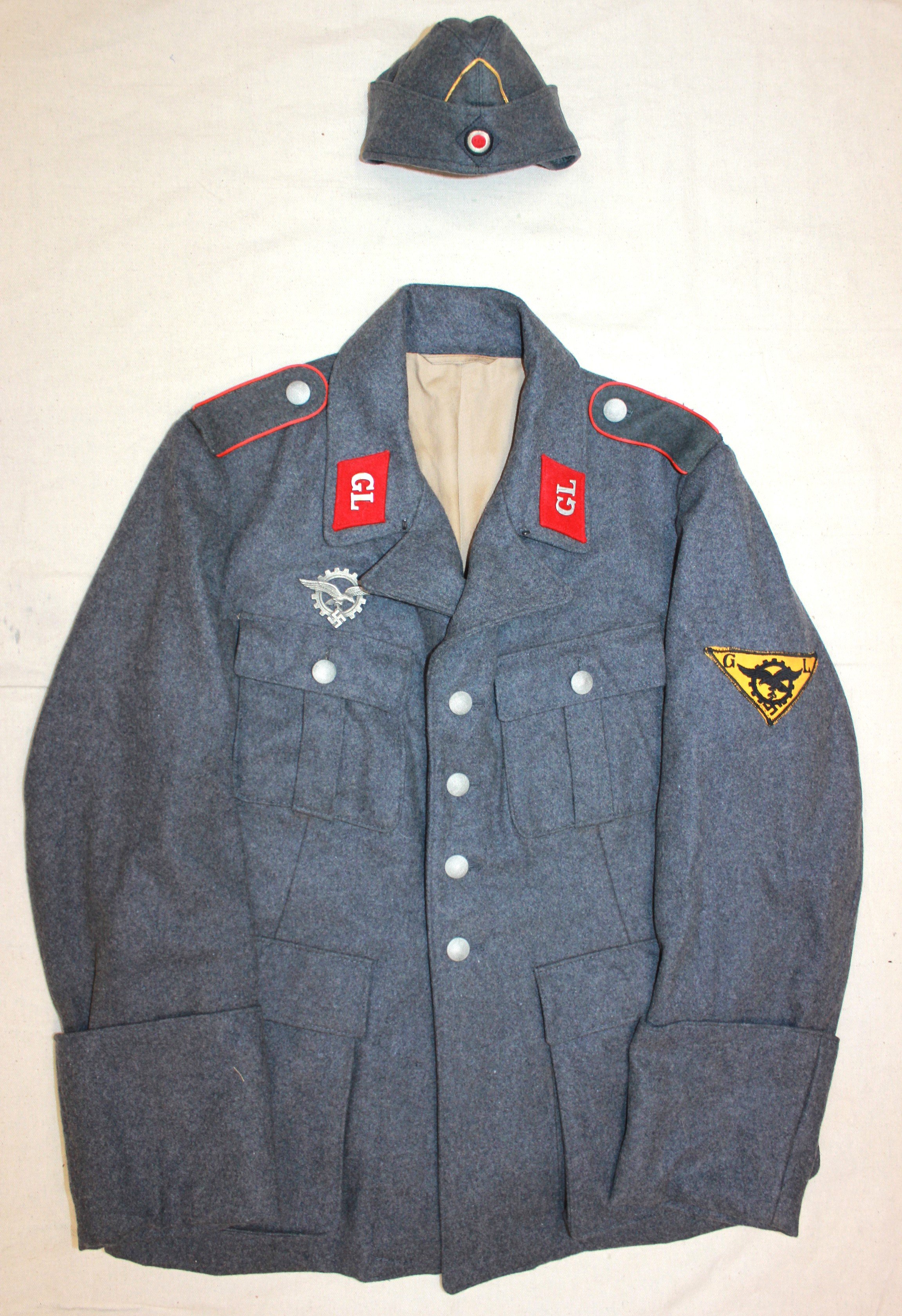
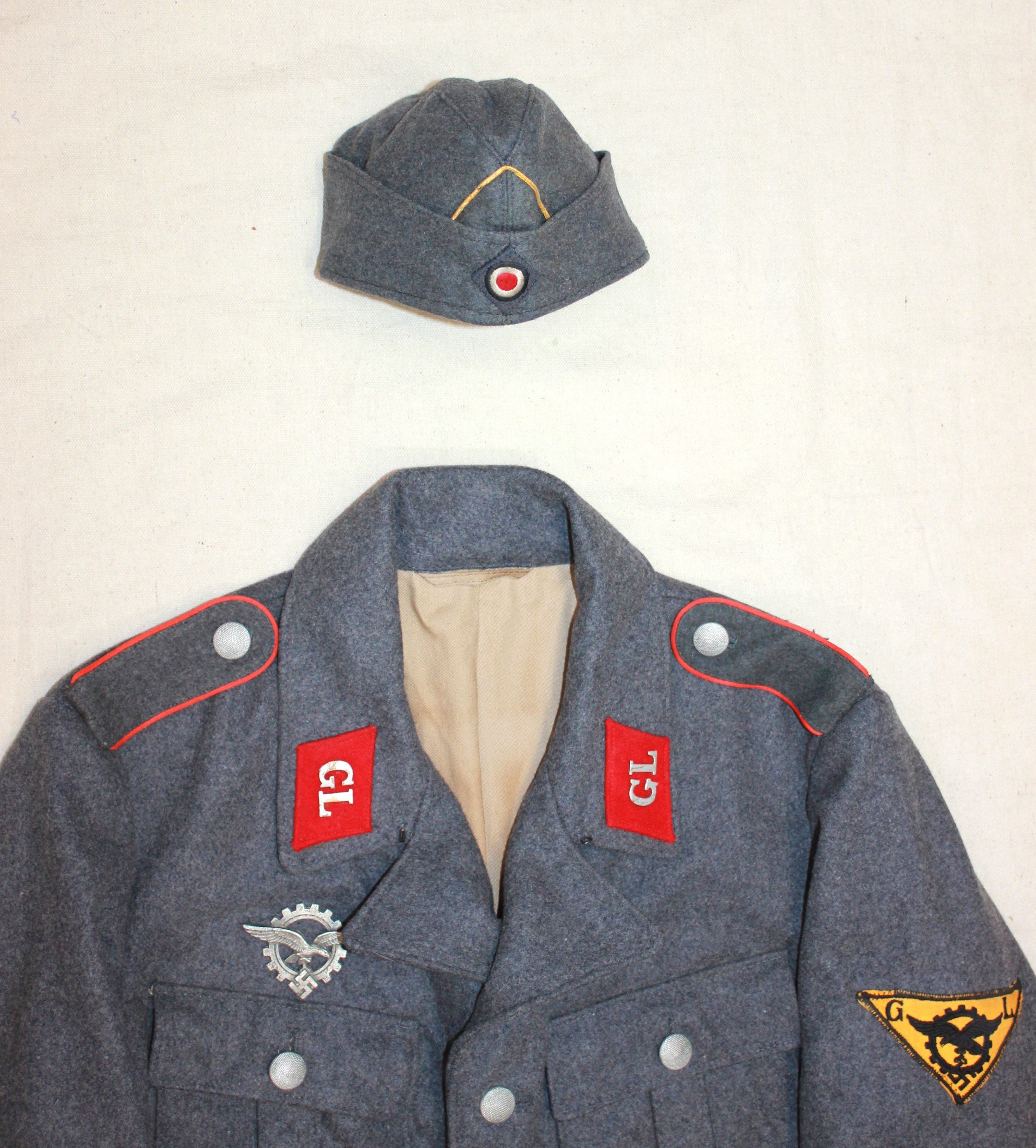
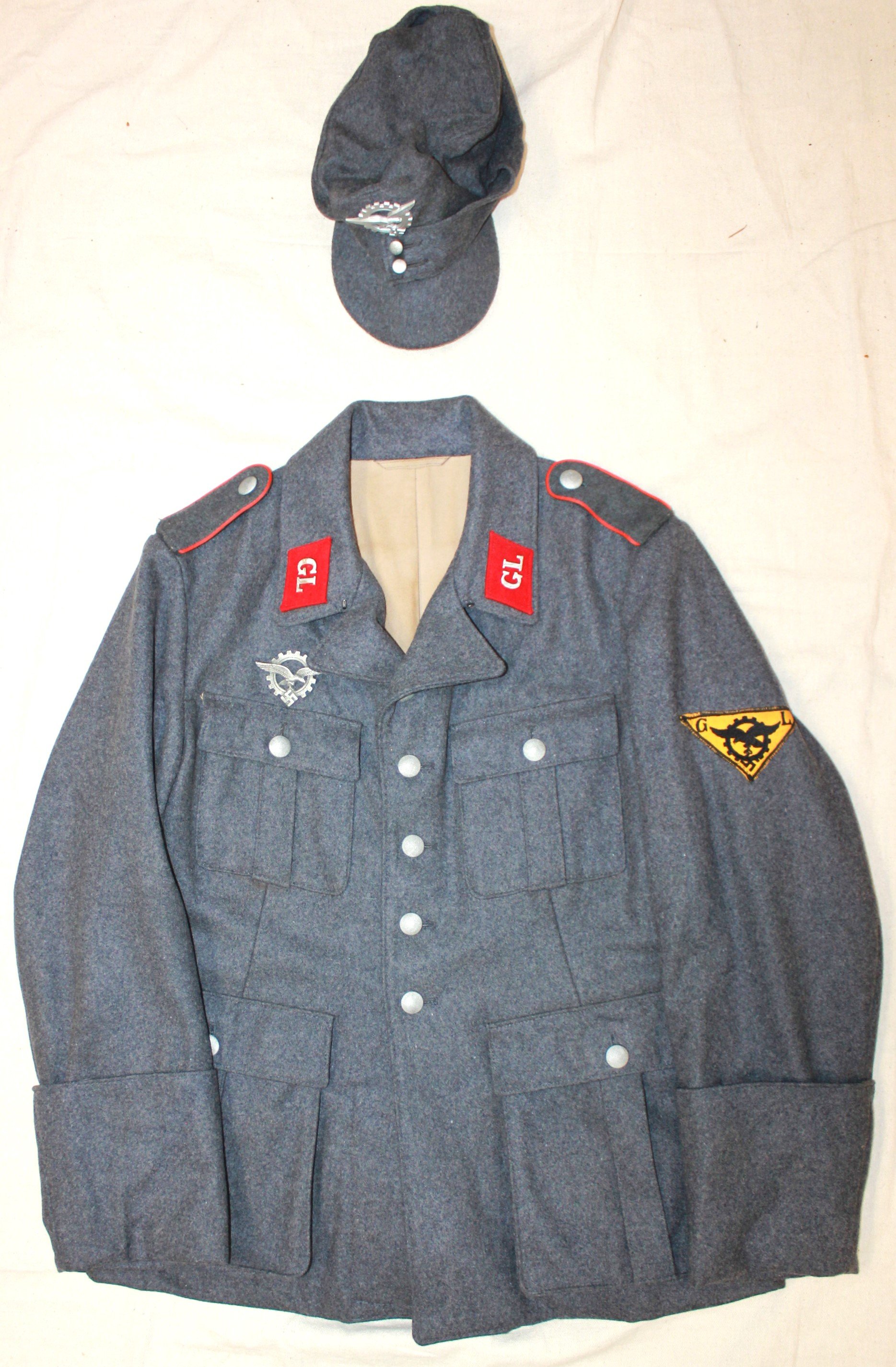
The development and testing required GL engineers to be in the field to physically check and monitor new projects. As the borders of the Reich expanded,d so did their areas of responsibility. Little information is available regarding the uniform regulations of the Generalluftzeugmeister.
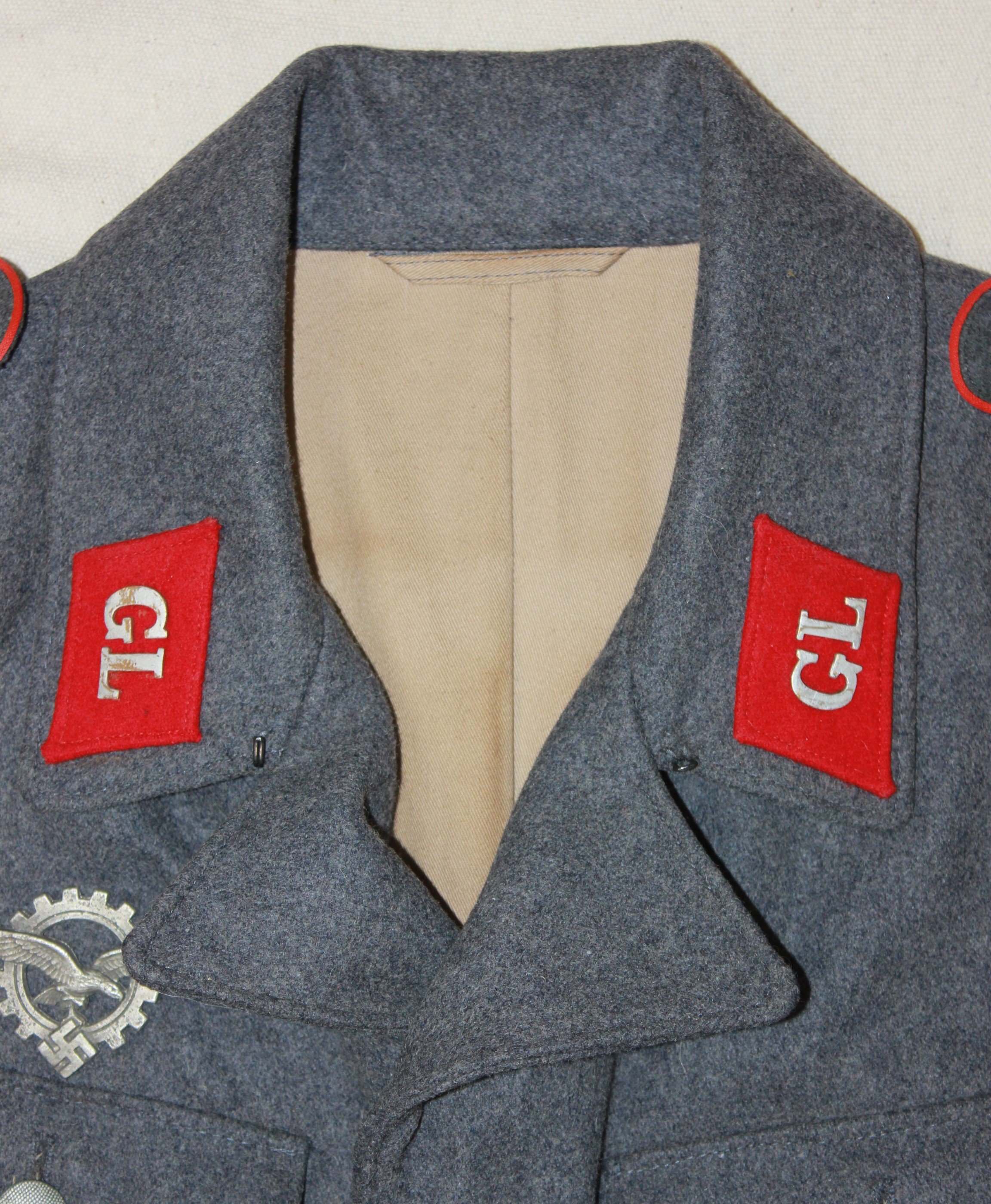
Period and collection photos show various combinations of insignia worn. A uniform in dunkleblau wool was also issued. The distinguishing insignia is the unique Industrie Abzeichen which had the Luftwaffe Adler imposed upon an industrial cogged wheel.
The Udet-Boje the Luftwaffe's Rettungsboje or Rescue Bouy, was designed to provide shelter for the pilots and crew of aircraft shot down or forced to make an emergency landing over the English Channel.
They were constructed under the direction of Generaloberst Ernst Udet, Generalluftzeugmeister, and became known as ‘Udet-Boje’. 50 Boje were deployed in the Channel, many off the Dutch coast. They supplied shelter, a means to signal that the buoy was occupied as well as a basic medical kit, iron rations, water, life jackets, as well as bunks and blankets.